Understand the Differences Between Code Signing Certificates and SSL Certificates for Validating Code Sources vs. Securing Network Communications
Code Signing Certificates and SSL Certificates may seem similar due to the use public key encryption. But, their applications and verification processes are completely different. Mainly used by developers and software publishers, a code signing certificate is used to sign applications, firmware, drivers, or executable files. Whereas, an SSL certificate encrypts the communication tunnel between a server and client and protects sensitive data, such as, login credentials and payment details.
To give you a clearer picture between the differences of these two digital certificates, we’ll compare them based on what each of them is used for, identity attachment, warranty available, validity type and expiry. Read on as we walk you through the differences between Code Signing Certificate and SSL Certificate.
What is an SSL Certificate?
Secure Socket Layer (SSL Certificates) which are used in creating encrypted connections over the internet between the server and the browsers. They are also used to build trust between the business owners and customers.
To assure your customers that the website is safe, most SSL Certificates will come with security seals which you display on different pages on your websites like login pages and checkout pages etc. The digital certificate will also give essential indicators like showing HTTPS on browsers instead of the insecure HTTP.
If you’re using high-level SSL Certificates like Organization Validation (OV SSL) or Extended Validation (EV SSL) your business will be verified.
SSL Certificates use PKI Infrastructure to ensure secure encrypted connections over the internet.
What is a Code Signing Certificate?
A Code Signing Certificate verifies the identity of a software developer or publisher and offers an assertion that the signed software has not been modified or altered. A digital signature and hashing are applied to software.
To access software, the developer will first sign his code with the private key. The end user’s system or software with the use of public key will decrypt the signature.
The primary role of the Code signing certificate is to ensure that an unknown user has not maliciously modified specific software or code.
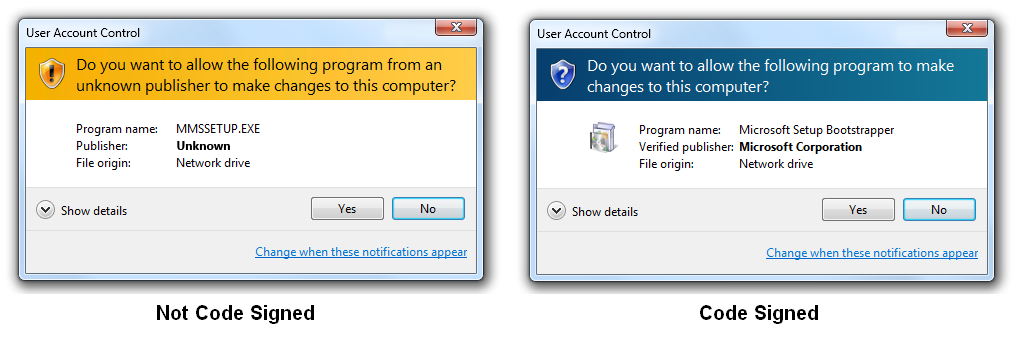
A software that’s not secured with code signing certificate will always display an Unknown Publisher warning for users when they attempt to download it. Usually, they’ll see a dialogue box that the code or software is from an unknown/unverified source hence can be dangerous if executed on their computers.
How SSL Works
- When the browser communicates with the server occupied with SSL (website), the browser requests server to identify itself.
- The server then sends its SSL certificate along with the public key.
- The browser from the list of root certificates checks the certificate against the list. The browser here, confirms the certificate revocation, expired status along with the valid common name. If the browser trusts the details after verification, it allows and sends back an encrypted symmetric session along with the server’s public key..
- Then, the server decrypts the received symmetric session with its private key and send an encrypted acknowledgement again with the session key and permit for the encrypted session.
- From then, all data will be transmitted in encoded format between the Server and Browser.
How Code Signing Works
- Code Signing certificate works on both public and private key as well Hashing. After finalizing the software, the developer will apply the private key to embed the digital signature.
- After finishing a piece of software, the software developer will use the Private Key to apply a digital signature.
- The digital signature then hashed (put a set on the code) with the remained code.
- Upon downloading the software, the user’s system will verify the digital signature.
- Once the signature is verified, the system will create a hash for the software. Now both hashes created by the system and the initially created by software publisher should be the same.
- If both hashes match, the software code is not altered since a software developer signs it.
Comparisons between SSL Certificates and Code Signing Certificates
To give you a clearer picture between the differences of these two digital certificates, we’ll compare them based on what each of them is used for, identity attachment, warranty available, validity type and expiry.
Purpose
The primary purpose of installing an SSL Certificate is to encrypt all the information shared on a website. It achieves this through 256-bit encryption which ensures that confidential data like login details cannot be intercepted and read or maliciously modified by a would-be-interceptor like man-in-the-middle attackers.
The Code Signing Certificates, on the other hand, do not encrypt the software but hashes and signs the software. This technology works in such a way that if someone tries to modify the codes in the middle, the end-user is alerted that it is not the original version of the software they wanted and may be dangerous to install them on their computers or mobile devices.
Besides, it also alerts the developer about the malicious tampering so he can delete the affected code of a software and publish a good one.
Documents Verification
It’s worth noting that for both digital certificates, a CA must verify the applicant. For the SSL Certificates, your CA will check that you’re the real owner of the domain name you’re ‘trying’ to safeguard.
For a necessary certificate like the Domain Validated (DV) SSL Certificate, the validation process is shorter, and you can complete it over the email. For a certificate like Extended Validation (EV) SSL or Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificate though, the verification process is a bit strict, and you’ll be required to submit information business registration documents along with physical address verification along with domain verification.
For Code Signing Certificates though, when applying for the certificate as a business, you will need to give your CA a business registration document that shows contact number, business address. At the same time, for an individual developer, you need to submit a notarized form to confirm your government-issued photo verification and a call verification.
Once this process is complete, the digital certificate will let you insert a digital signature into your code or software. This signature is necessary because it helps your customers to prove that:
- The software is genuine.
- Eliminate the ‘unknown/unverified’ security warnings that may scare off your users from downloading the software.
- It also protects your code through cryptographic hashing to preserve its integrity.
Validation Required
SSL Certificates offers Domain Validation (DV), Organization Validation (OV) and Extended Validation (EV).
DV SSL Certificates are designed only to validate the domain name. They do not provide extra information regarding the web server or the person who owns the website.
OV SSL Certificates validate the organization and domain ownership.
EV SSL Certificates validate the business identity and domain ownership and legal existence of a business and offers HTTPS and a padlock in the address bar along with the highest validation.
Code Signing Certificates have two validation types, i.e. Organization and Extended Validation certificate.
Check Identity
For SSL certificate, you can click on the padlock and check the certificate details like certificate issuer, domain name, issue date, expiry date, etc. The identity assurance ensures customers that they are on the legitimate site and not a fake one.
For a Code Signing certificate, once the vetting process is completed, there will be a verified digital signature on software. When a buyer sees the publisher’s name, he/she gets the assurance that the software is not from the unknown publisher but a verified developer.
Warranties
SSL Certificates have varied warranties (starting from $10,000) depending on the type of the certificate you’ve purchased. The Code Signing Certificates, on the other hand, usually have $50,000 warranty (Thawte Brand) attached to them.
Expiration
SSL Certificates have a lifespan of one year and will show a ‘not secure’ warning when the users visit your web pages once the SSL has expired. On the other hand, the Code Signing Certificates can be issued for up to three years. It may also indicate an ‘unknown/unverified publisher’ security warning when users try to download your software once the certificate has expired.
However, if you use time stamping for Code Signing certificates, your name will still be visible even after the certificate has expired. The time-stamping feature here is a digital signature which only you can add to the software with the help of a private key.
Most publishers prefer it because even after your code signing certificate has expired, your customers will still be able to ascertain that you were the original publisher of the software and that you signed it when it was still valid.
SSL Certificate and Code Signing Certificate- The price Factor
At the basic level, the pricing for a Domain Validated (DV) SSL Certificate begins from $5.99/yr. The Organization Validated (OV) and Extended Validated (EV)SSL Certificate pricing starts from $29.00/yr. and $49.00/yr. respectively.
If you wish to secure unlimited subdomains, the Wildcard SSL Certificates would be a worthwhile option. The pricing for Wildcard SSL Certificates begins from $26.00/yr.
When it comes to the code signing certificates, the pricing range for an Individual/business authentication Code Signing Certificate begins from $226.10/yr.
Comodo Code Signing |
Comodo Positive SSL |
|
| Used to | Code and File Signing (Microsoft executable apps, Java, Adobe, Mac, Microsoft Documents ) | Secure website |
|---|---|---|
| Price starts from | $226.10/yr. | $8.00/yr. |
| Add To cart | Add To cart | |
| Algorithm | SHA-2 Enabled | SHA-2 Enabled |
| Validation Type | Individual / business authentication | Domain validation via email |
| Issuance Time | 2-3 Business Day | 5 minutes or less |
| CSR Encryption | 2048-bit | 2048-bit |
| Mobile & smartphone support | ||
| Browser compatibility | ||
| Client OS compatibility | ||
| SSL Reissuance | unlimited free reissues for certificate lifetime | Yes (Free Cost) |
| Warranty | – | $10,000 USD by Comodo |
| Refund Policy | 30 Day 100% money back | 30 Day 100% money back |
| Add To cart | Add To cart |
Final Word
While the SSL Certificates and Code Signing Certificates serve very different purposes, they’re the only foolproof ways of winning the trust of your target audience. If you’re a software developer who makes codes/software or wishes to secure your website, both are necessary.
The SSL Certificates will boost the confidence of users who deal with your website while the code signing certificates will help you get rid of those ‘scary’ warnings that may make a customer lose trust in your software/brand.
Related Articles:
- What is Code Signing Certificate? How Does it Work?
- The Detailed Guide to Code Signing Certificate Best Practices
- Free Code Signing Certificate – Where Can I Get It?
- EV Code Signing vs. Regular Code Signing : Decode the Differences
- Code Signing Certificate – Upgrade Security with 3072-bit Key Length