Learn How S/MIME Certificates Protect Email Privacy and Prevent Spoofing
A digital certificate known as an S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) certificate is utilized to increase email communication security. It offers features for encrypting and digitally signing email messages, guaranteeing secrecy, trustworthiness, and legitimacy.
S/MIME certificates are an important resource for enhancing email security, offering strong encryption and authentication measures to safeguard confidential data and build confidence in email interactions.
This article aims to help you secure your business communications and sensitive data by securing your mail using a S/MIME certificate.
What Is a S/MIME Certificate?
S/MIME is an acronym for Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension. S/MIME certificates are usually referred to as email signing certificates or personal authentication certificates. Essentially, this email security protocol has a two-pronged action.
- To help the email recipient confirm the sender’s identity.
- To prevent unwanted parties from reading, tampering, intercepting, or compromising with the contents of the mail, whether at rest or in transit.
S/MIME certificates have been around for quite some time and have successfully addressed security issues and vulnerabilities. In addition, S/MIME certificates have evolved and become fool proof over the years to address security issues like EFAIL (a security vulnerability that affects end-to-end encryption solutions).
How Does an S/MIME certificate work?
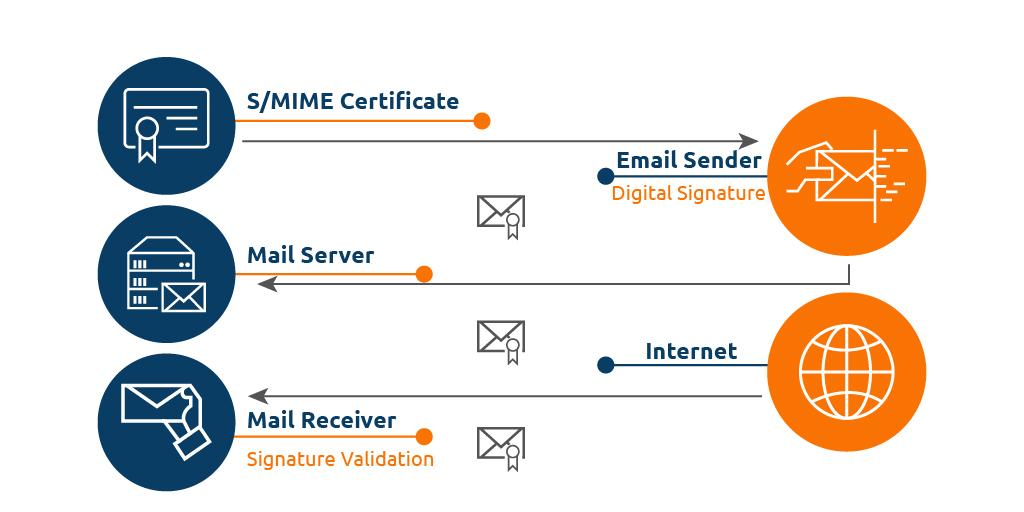
S/MIME certificate works on two functions: Encryption and Digital Signing. Below we have discussed how S/MIME certificate works.
Digital Certificate and Keys:
An S/MIME certificate is a digital certificate that works on a public and private key pair and includes the details of the certificate holder. A Certificate Authority (CA) issues this certificate, which includes a private key, public key, certificate authority information, user information.
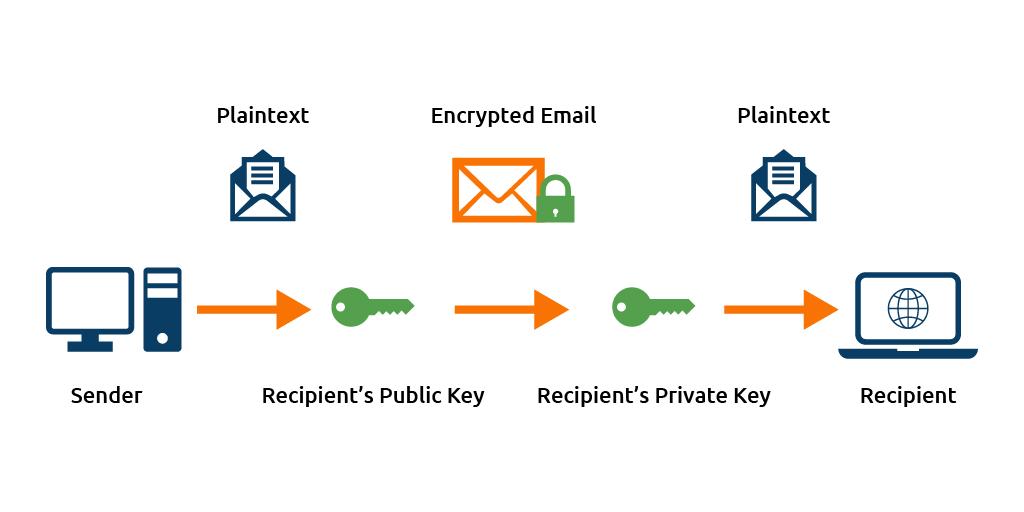
Encryption Process:
The main object of an encryption is to ensure that the intended person can receive and read the email.
- Obtain Recipient’s Public key: When creating an email, the email client retrieves the receiver’s public key from their certificate.
- Email Encryption: An email client uses receiver’s public key for email encryption. With this process, the plain text is transformed into an unrecognized format. Then the encrypted email is sent to the receiver.
- Email Decryption: The receiver then uses a private key to decrypt the email to read the email content.
Digital Signing Process:
This process confirms that the message has not been altered and it confirms the sender’s identity.
- Create a digital signature: The email content is hashed with cryptographic hash function in which a fingerprint or unique hash value is created. Then, the hash value undergoes for encryption process using the sender’s private key. It creates a digital signature, which is attached to the email. After that, the email is sent to the receiver.
- Signature Verification: The receiver’s email client decodes the digital signature with sender’s public key. Thus, the receiver receives the original hash value.
- The receiver’s email client hashes the email and compares it with the decoded hash value. If both hashes match, it shows that email content has not been modified.
Certificate Validation:
To ensure that the S/MIME certificate comes from a trustworthy source, the receiver email client performs the tasks below.
- Certificate chain verification to ensure that the certificate is coming from a trusted CA like Comodo SSL or Sectigo SSL etc.
- By checking certificate revocation list in Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) or using the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP), it confirms that the certificate is not revoked.
- It also checks the validity period of a certificate.
Key features of S/MIME certificate
When using a S/MIME certificate for email applications, you get a host of cryptographic security features.
Authentication
It means verification of the identity of a computer user or a website.
Message integrity
This is the assurance that all the contents and data present in the message are not tampered with. The confidentiality of the message is critical. The decryption process involves verifying the original contents of the message and ensuring that it has not changed.
Use of digital signatures invoking non-repudiation of origin
This refers to a situation where the digital signatures validate the original sender and his identity so that there is no dispute about the same.
Data privacy
No unintended third party can cause a data breach.
Data security with the use of encryption
It refers to the processes discussed above where a combination of public and private keys representing asymmetric cryptography ensures data security.
A S/MIME certificate designates the MIME type. The MIME type refers to the enveloped data. The entire MIME entity is prepared, encrypted, and packed into a digital envelope.
How does a S/MIME benefit your business?
In today’s digital world, running businesses requires communications to be strong and the platforms to be resilient. Since the reach of the emails is undoubted, protecting them with the help of a S/MIME certificate will have several positive implications for your business.
Business Reputation
S/MIME certificate protects business reputation by ensuring that the email does not contain any virus and received from official email address. With this certificate, there are no chance of email tampering and establishes a trust between a business and users. For an additional layer of brand authentication, businesses can also use a DigiCert Verified Mark Certificate (VMC), which displays the company’s logo in supported email clients. While S/MIME secures the message, a VMC reinforces brand credibility and visual trust in the recipient’s inbox.
Minimizing business risk
Having a S/MIME certificate ensures an additional security layer of sender identity verifications to combat email phishing techniques. According to ProofPoint research, 83% of surveyed global info security professionals claimed to be susceptible to phishing attacks in 2018. Message integrity is a crucial feature of email encryption techniques, and it helps in nullifying hackers who would want to intercept and tamper with your critical communications.
Avoiding compliance risks and associated fines
Businesses that store and use the personal information of consumers need to adhere to specific rules and regulations. Failure to comply with them would incur substantial fines. Using a S/MIME certificate would negate such possibilities.
Preventing identity thievery
Man-in-the-middle (MitM) hijacking is often about gathering confidential information like usernames and passwords and using your identity to create serious troubles later. Using an encrypted digital signature will reduce identity thefts.
Even if these hackers break the encryption, the entire content needs to be checked and matched for successful decryption, and the slightest change will trigger a warning message. Therefore, the S/MIME certificates will help your business conduct communication effectively without worry.
How does S/MIME address security vulnerabilities in email?
From the above discussions, it is clear that a S/MIME certificate is an end-to-end encryption solution for MIME data, a.k.a. email messages. The use of asymmetric cryptography by the S/MIME certificates prevents compromising the message’s integrity to a third party. In plain language, you hash the message by applying a digital signature. Then you encrypt the mail to ensure the confidentiality of the message.
According to GlobalSign- a company that provides specialized Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) solutions to enterprises, S/MIME uses public encryption to secure messages that can only be decrypted with the corresponding private key possessed by the designated mail recipient.
We can visualize the situation by stepping back in time. The use of wax seals on letters was unique identification proof of the sender while helping the recipient comprehend if the letters were tampered with. The S/MIME certificates operate on a similar concept.
There is a private key for the sender to digitally sign the mail he is sending. A public key then accompanies the email in transit. The recipient will use it to authenticate the sender’s digital signature and his own private key to decrypt the mail. This system of leveraging two different yet mathematically similar cryptography keys gives end-to-end encryption using ‘asymmetric cryptography.’ Without both the keys, the entirely encrypted contents of the email will be nearly impossible to crack.
S/MIME involves one of the three main types of encryption quintessential for emails.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS)
- Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension
- Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)
How can you send encrypted emails?
Some organizations and individuals make use of secure email service providers to send secure emails. These service providers, like ProtonMail, might help you send and receive private messages for free, but the downside lies in the fact that both sender and receiver need to have the same account. This is a general drawback for end-to-end encryption service providers.
Apart from this challenge limiting the utility of email platforms for business, there exists a far graver one. Even to this day, these so-called secure email service providers are susceptible to cyber-attacks. VFEMail is a prime example of a secure email service provider that succumbed to a cyber-attack after 20 years of operation.
The most effective way is to leverage a S/MIME certificate to sign and send encrypted emails digitally. The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) considers this mechanism as secure public-key encryption, and it is also recommended as a “protocol for email end-to-end authentication and confidentiality” by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
How to implement S/MIME?
Although S/MIME deployment may seem like an uphill task, we will help you configure S/MIME for Outlook 2010 or later.
Import S/MIME certificate
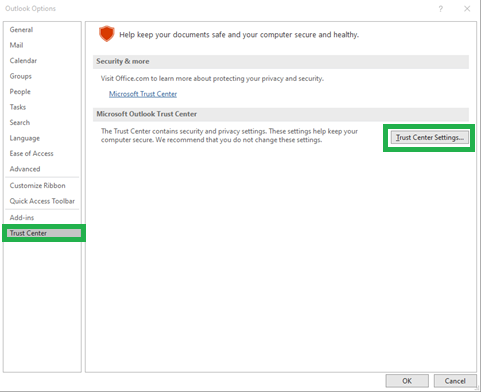
- Open File>>Options in Outlook 2010/2013
- Now, click on Trust Center > Trust Center Settings under Outlook Options.
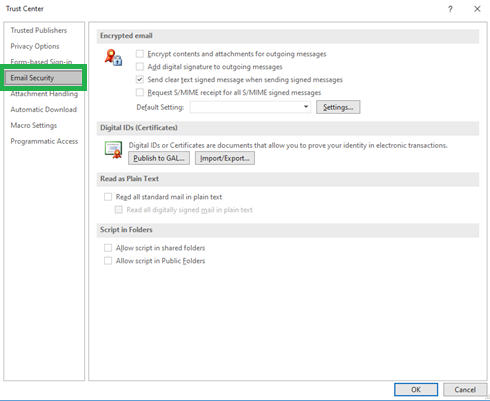
- After that, click on “Trust Center Settings” button and click on “Email Security” tab on the left side.
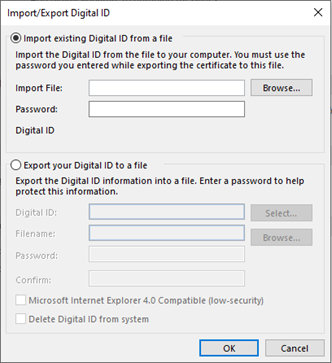
- You will have Import/Export button under Digital IDs (certificates) label in the middle of the screen. Click on it.
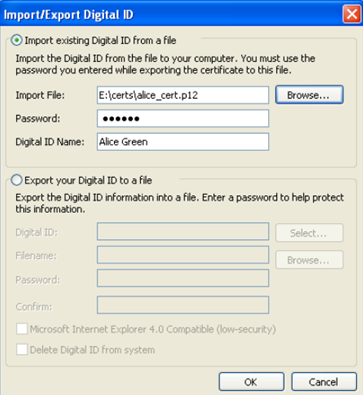
- In the Import/Export Digital ID interface, Browse PKCS12 certificate file and click OK. Keep digital ID name and use password used during export of certificate.
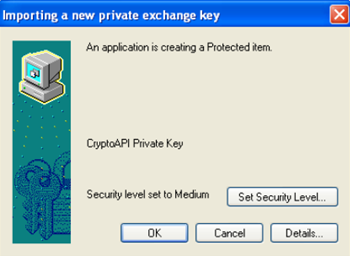
- Now, select security level for storing private key and click OK.
Assign the Certificate
- Open Outlook 2010/2013 and access File>>Options
- Click on “Trust Center Settings” button and select “Email Security” tab on the left side.
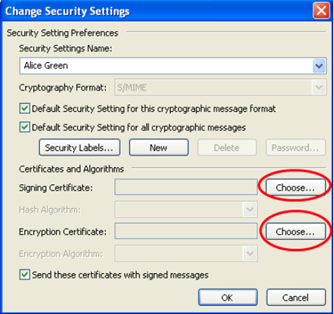
- Click on “Settings” under “Email Security” option as showing in above image.
- You will have a “change security settings” where you can choose signing and encryption certificate.
- First click on choose button against signing certificate, there you can choose signing certificate from imported certificate and Click OK.
- Again, click on choose button against Encryption certificate, there you can choose encryption certificate from imported certificate and click OK.
- After choosing both certificates click OK button and return to the Trust Center screen.
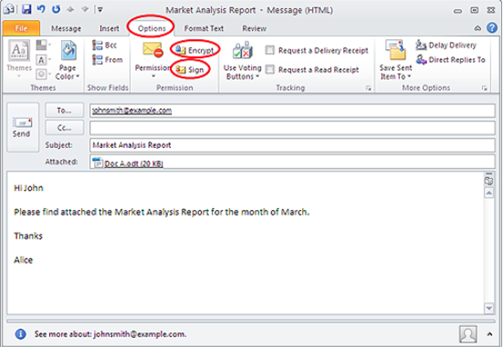
Signing and Encrypting Individual Emails
- First compose mail in outlook and click on Options in menu bar and click on “Encrypt” and “Sign” button as per your requirements.
- When you send email, it will be encrypted and signed as per your selected option.
Signing and Encrypting All Mails by Default
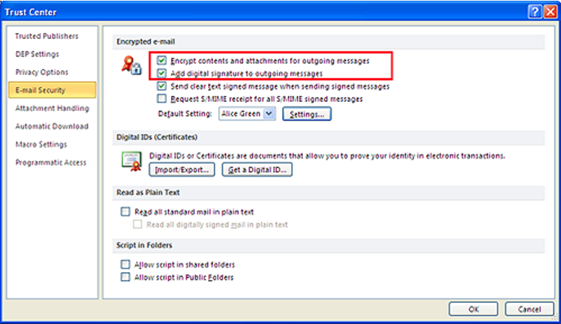
- Open Outlook 2010/2013 and browse File>> Options.
- On the left side, click on ‘Trust Center’ and then click on ‘Trust Center Settings’ on the right side.
- Choose ‘Email Security’ on the left side and select below two boxes named as:
- Encrypt contents and attachments for outgoing messages box (To encrypt each message)
- Add digital signature to outgoing messages box (To sign each message)
- Click OK button.
S/MIME Support
Here are some of the most used email clients that support S/MIME.
- Apple Mail
- iPhone iOS Mail
- IBM Notes
- Gmail
- Microsoft Outlook or Outlook on the Web
- Mozilla Thunderbird
- MailMate
- CipherMail
Although a S/MIME certificate has existed for a long time and is supported by most email clients, the cons of its usage involved cumbersome implementation due to the sender and recipient’s public and private keys. As a result, its use was limited to highly confidential government communication and those initiated by tech geeks.
However, with the rise of automation tools for implementing and managing S/MIME certificates, its adoption trend has improved. The awareness that S/MIME certificates help your business by protecting in-transit and at-rest data has outweighed the cons.
S/MIME Validation Levels
S/MIME certificates have three validation levels. In addition, every Certificate Authority (CA) has its unique classification. Here is a simple list that clearly explains the validation levels and provides enough information to select the best S/MIME certificate that caters to your needs.
Basic Level
A basic level validation requires a domain validation where a verification link is sent to prove domain ownership. Once the certificate is installed, it will show verified email address along with digital signature on the certificate. It also assures users that the email is from legitimate sender.
Pro Level
In a pro level validation, it requires identity verification and domain validation process. The identity verification process verifies you as an employee. It requires government issued any proof like driver’s license and company email address. After verification, the authority issues email signing certificate and your name will be shown on email address.
Enterprise Level
In Enterprise level, the certificate authority checks domain validation, identity validation and organization validation. The authority performs organization authentication, verifies locality, tele verification, and a verification call. Once all details are confirmed, the authority issues a certificate with a digital signature, which includes verified email@address.com, first name, last name, company address and its name.
Closing thoughts
Implementing a S/MIME certificate across your organization’s email platform will ensure relieving the pain points of email security and data confidentiality. Apart from the assurance that your organization identity is verified, you can conduct business in a free spirit knowing your messages are encrypted and the integrity of your attachments is also secure.
Related Articles
- How to install an S/MIME Certificate in Outlook
- Wildcard SSL vs Multi-Domain (SAN) SSL Certificate – Differences Explained
- The Difference Between DV, OV, and EV SSL Certificates
- Code Signing Certificate vs. SSL Certificate – What are differences?
- What is the Sectigo RSA Domain Validation Secure Server CA?
- Digital Signature vs Electronic Signature – Key Difference Explained