Understanding PKI Role in Certificate Lifecycle Management
Everyday life depends on the internet, from online banking to shopping online in this digital world. However, with the increase in the use of networking, cyber-crimes have also increased, which results in the stealing of sensitive data and the spreading of malicious software through unnatural links. Here comes the importance of Public Key infrastructure. PKI is based on data encryption which secures online data from cyber-attacks. This document covers topics such as the application of PKI, use of PKI, components of PKI, management of PKI, and best practices of PKI.
What is Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)?
PKI, which is Public Key Infrastructure, plays a significant role in network security. It works based on data encryption. It contains a pair of keys called as Public-Private key and digital certificates. These keys are used for encryption and data decryption for secure information transfer online. These two keys can be used by applications, people, and devices.
The digital certificates are used to verify the authenticity of particular software or program. This Public Key Infrastructure is mainly used to secure the devices or network from malicious cyber-attacks.
A system that includes policies, institutions, and technologies that are used to handle the distribution, authentication, and revocation of a digital certificate is known as Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
Uses of PKI
Public Key Infrastructure is used to make the secured online interactions by establishing and encrypting the endpoint’s identity and the data flow through the network’s communication channels.
The PKI is used for various purposes. They are,
- Digitally signing the software or applications to prevent them from cyber-attacks.
- Recovery of security passwords.
- Used for a description of files.
- For network security.
- For the protection of server-hosted communication.
- Authentication of identity such as smart cards.
- Used for the security of IOT (Internet of Things).
- For encrypting the emails to secure the privacy of the communication.
- For the security of communication in websites.
Applications of Public Key Infrastructure
The Public Key Infrastructure security has various applications in day-to-day life. It is used in many ways to secure online transactions. How PKI can be used are,
- Securing emails for confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. For this purpose, PKI uses S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) to transfer encrypted mails with digital signatures.
- To protect web communications such as retail transactions. This is done by the SSL handshake phase, which is to verify the identities of communicating parties using digital certificates.
- PKI-based encryption and digital signature are used along with VPN network layer security protocols for confidentiality. A VPN is a private data communication that uses a public network.
- It is also applied in smart card authentication, which is used for identity verification in various private enterprises as well as in government sectors.
Components of Public Key Infrastructure
-
Public Key
A public key is an encryption key dispersed to the public. It does not require safe storage. The sender uses a public key to encrypt the messages, and the messages encrypted using the public key can only be decrypted by using the relevant Private key.
-
Private Key
As the Public key encrypts the messages, they can only be decrypted by the relevant Private key. Hence the Private keys are used by the recipient to decrypt the messages. This can be done by getting the ownership of the Public-Private keys. These keys are a sign of authenticity. They are provided along with digital certificates by the trusted certificate authorities.
-
Certificate Authority (CA)
The main role of the Certificate authority is to issue Digital Certificates, which are used to verify that the name printed on the certificate is the original owner of the public key. Certificate management for PKI will be handled by CA, along with the certificate life cycle management phases.
- Root Certificate Authority
The Root Certificate Authority is a trusted Certificate Authority that verifies the identity of the owner and signs the root certificate that is distributed to users. - Intermediate Certificate Authority
It is also a trusted Certificate Authority used to link the root certificate and the client certificate. SecureW2’s PKI always uses the intermediate CA to generate client certificates to authenticate Wi-Fi.
- Root Certificate Authority
-
Registration Authority
This RA helps in the PKI cycle to verify the body requesting the certificate is legitimate or not. Then the request is allowed to reach the certificate authority.
-
Certificate Store
It stores digital certificates and contains certificates from various certificate authorities. In addition, the certificate store has LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol), which classifies the entries of the certificates.
-
Hardware Security Module (HSM)
It helps to improve the security of the Public Key Infrastructure when imposed. It is a kind of device which secures and handles digital keys and helps to build a safe PKI infrastructure. It also manages the complete lifecycle of cryptographic keys. HSM is not a mandatory part of PKI, but it enhances its security.
-
Certificate Revocation List (CRL)
The certificate authority will maintain the certificate Revocation List. It contains a list of certificates revoked by the Certificate Authority before they expire. This CRL is useful when a device that contains a certificate is stolen. It consists of a RADIUS server that rejects a connection from a device with a revoked certificate’s serial number.
How Does Public Key Infrastructure Work?
The Public Key Infrastructure works on data encryption. It uses Public-Private Keys and Digital Certificates for the secure transfer of data. The PKI addresses four main issues that occur during electronic transmission. They are,
- To encrypt the document’s contents so that the document is kept confidential.
- To make sure that the document is not modified in transmission.
- To verify the owner of the document.
- Ensure that the end-user can receive the data and able to decrypt it.
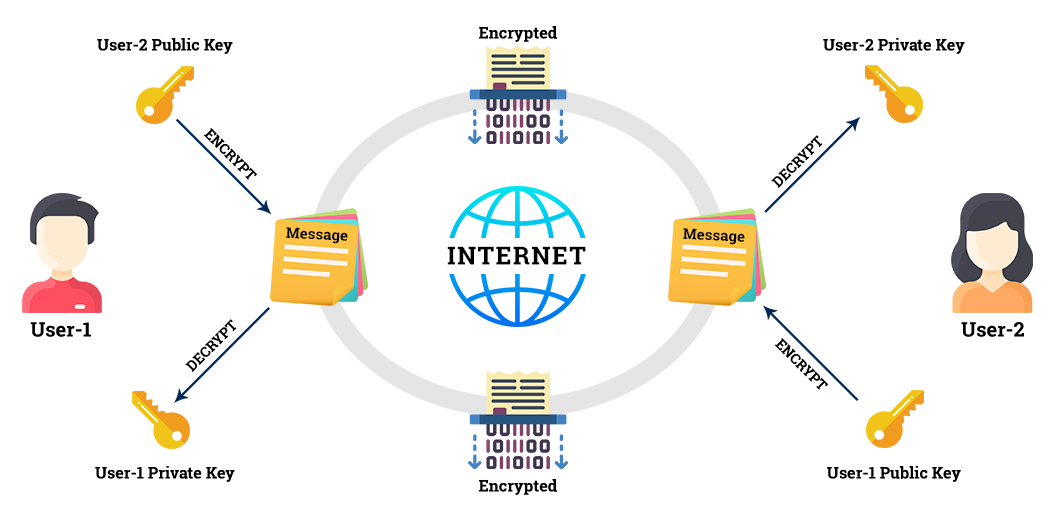
Let’s see an illustration of How PKI works.
For example, Person-A wants to send a confidential message to Person-B through electronic communication. So, Person-A has four major issues to be addressed before transferring the message.
-
Securing the Messages:
This step ensures that the document is protected from interpretation by a third party. Person-A will initially encrypt the document with Person-B’s public key. It makes sure that the document is encrypted, and only Person-B can decrypt the message using his or her private key. But this does not guarantee that the transferred contents are not altered.
-
Digesting the Message:
It ensures that another person does not modify the transferred content. Person-A performs a hash function on the content. This hashing is known as a message digest. Hashing is a process in which the original contents are replaced by computational value to maintain the confidentiality of the content. When Person-B performs the same hash function during the decryption of the document, he or she gets the hashed value that can be compared with the content sent by Person-A and make sure the document is not altered.
-
Digital Signature:
To prove that the document is authenticated from Person-A, he or she must use a digital signature. The digital certificate contains the name and details of the original owner of the document. The sender’s private key is applied to the message or document in such a certificate. This is called signing. So, by using the digital certificate, Person-A can verify whether the document is originally from Person-B or not.
-
Non-repudiation Services:
Each Public key has a corresponding private key which is mathematically linked. These keys are used along with the digital certificates to send and receive messages confidentially without any interference by a third party. This ensures that Person-B can receive the original document and cannot deny the fact of receiving it.
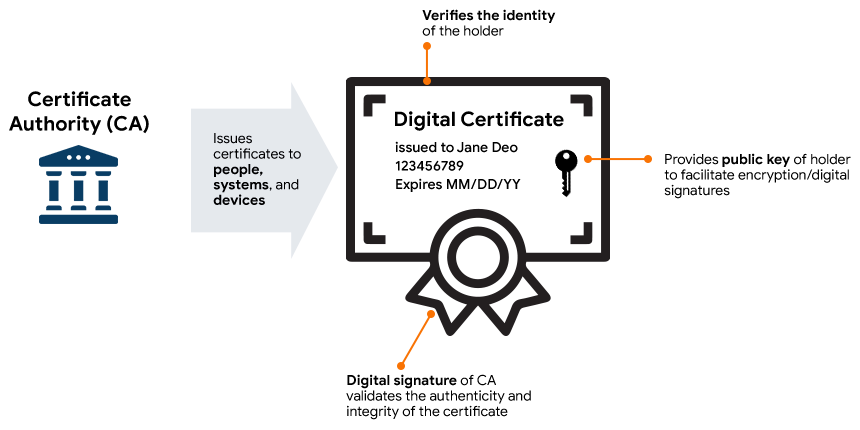
Role of Digital Certificates in PKI
Digital certificates are the standards for digital ID systems’ security protocols and data transfer. They are used in Public Key Infrastructure for safe online transactions among people, systems, or devices. The two primary functions of digital certificates are,
- To verify the identity of the sender and receiver of the message.
- To facilitate the encryption and decryption of transferred messages.
Even though the software developers can create their own digital certificates, it is easier and more reliable to use a trusted third party as the Certificate Authority.
The digital certificates are used to guarantee that the content of a program or software is from an authentic source and does not contain any malicious programs in it. A digital certificate consists of various information such as,
- Name of the owner of the certificate.
- The issuance and expiry date are used to determine the certificate’s lifetime.
- The public key is used for data encryption.
- The Certificate Authority provides a digital signature.
There are three types of digital signature used in Public Key Infrastructure management. They are,
- Individual Digital Certificates:
It is used to identify a single person. In addition, the certificate contains personal information which implements access to sensitive data. - Server Digital Certificates:
It is used to verify a server. The certificate includes the hostname or IP address. It secures one or two-layer SSL communication over a network. - Encryption Digital Certificates:
It encrypts the data using the public key of the receiver. Various digital signature is provided by different Certificate Authorities.
What is PKI Management?
PKI management includes many tasks and responsibilities required for running an efficient and effective Public Key Infrastructure. The PKI management includes
- managing digital certificates,
- authorizing public and private keys,
- storing the private keys to protect the keys from loss or misuse.
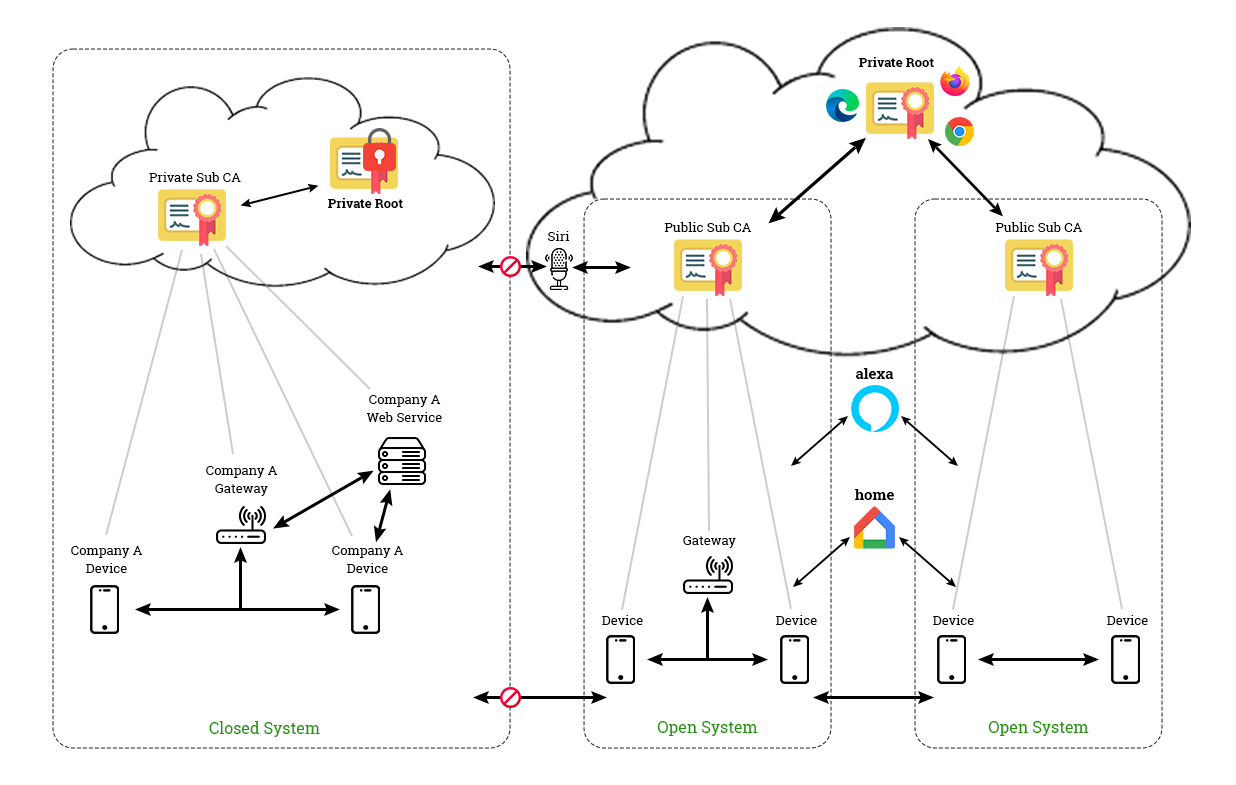
The Significance of Public and Private PKI Factor in the PKI Management
There is a difference in managing and using the Private and Public Certificate Authorities or CAs. This is because public PKI and private PKI serve different purposes in which Public CA certificates and keys are used in public-facing environments while Private CA certificates and keys are used for internal environments.
-
Public Certificates:
A publicly trusted Certificate Authority issues the public PKI certificates from its trusted root. Such certificates are automatically trusted by browsers, operating systems, and major applications, which form a universal certificate chain. It is also known as the “chain of trust,” and displays verified messages in the browser.
-
Private Certificates:
A private Certificate Authority issues the private PKI certificates. Generally, these certificates are not trusted by browsers or other applications. To gain trust, the private root must be distributed manually. The private certificates are used to secure devices without IP address/hostname/identity, such as IOT devices.
But it is not necessary to choose between the two certificates as many companies use a hybrid public-private PKI approach. Therefore, it benefits from public certificates in external environments and private certificates for internal environments.
Why PKI Lifecycle Management of Certificates and Keys is Paramount?
Improper maintenance of the keys and certificates of a PKI may lead to various issues which may affect the management in many areas such as security, compliance, customer trust, etc. In addition, this can result in displaying error messages on public websites.
In PKI, the management of certificates and keys goes hand in hand. A digital certificate without a secured key is pointless, and a key is of no use without a valid certificate. To avoid mismanagement risks, organizations must evaluate whether to handle PKI internally or partner with a reliable PKI solution provider.
Public Key Infrastructure Lifecycle Management Best Practices
Before using the Public Key Infrastructure for secure online data transfer, it is important to understand the best practices of PKI management. This saves the company or organization from future problems and helps for the efficient functioning of PKI. The few major best practices are as follow
-
Appropriate Planning:
It is important to have a proper plan for the Public Key Infrastructure management before converting it to a working model.
-
Allocation of Responsibility:
The easy way for PKI management within the organization is to decide whether to handle all the work internally or outsource a few. However, it is also important to define the responsibilities of each employee in an organization. This results in accountability for each work which reduces fallacy.
-
Using Updated Security Protocols:
Adapting to the current security protocols plays a crucial role in the smooth functioning of PKI management.
-
Trusted Certificates:
To secure digital certificates from a trusted Certificate Authority. It is not good to use self-created keys and certificates for several reasons. They are
- The self-created certificates are not as strong as those issued by a Certificate Authority. This makes them easy to crack and fake the certificates.
- A proper storage facility may not be used for such certificates.
- As they are self-created, they can be difficult to discover, which leads to vulnerabilities in the blind spot.
-
Efficient Certificate Management:
Consistent certificate management is significant in PKI. It includes
- Revoking or suspension of certificates when required.
- Clearing of old and unused certificates.
- Creating a systematic approach for the renewal and expiration of certificates.
-
Using Public-Private Keys that are Long:
The Public Key Infrastructure works based on Public-Private keys, which are used to encrypt and decrypt the data transferred online. There are two ways for a cyber-criminal to get a key, either steal or guess it. The length and size of the key determine the difficulty of guessing the private key. If the key is long and complicated, it becomes difficult to crack it by reverse engineering.
-
Proper Storage Facility:
Mostly, it becomes easy to steal the keys and certificates as they are stored in the spreadsheet as plaintext, on a flash drive, on a normal hard drive, or any other easily accessible storage. The storage does not have so much as a Hardware Security Module (HSM) to protect it. However, a few measures can prevent stealing keys and certificates.
- Since public-private key pairs and digital certificates are indispensable in working a PKI, they must be stored in secure storage to safeguard from theft by cyber-criminals.
- The access to the storage of such sensitive data should be restricted to as few persons as possible.
- Ensuring that the keys are stored under the FIPS 140-2 LEVEL 3 system is mandatory.
- The storage methods such as key stores (OS and Browsers), key vaults (related third-party services), cryptographic tokens (detachable drives), Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) should be there.
Among the storage methods, HSMs are widely used by many businesses to store their keys. They are physical pieces of hardware that must store in a secured location and supports various applications and PKI management automation tools.
-
Shuffling PKI Certificates and Keys Frequently:
To ensure electronic data security, it is essential to frequently change the keys and the certificates. The shuffling is a counteract to theft or cracking of keys and certificates. Furthermore, even if the hacker got access to them, it would be expired soon.
-
Administering Root Key:
The Root Certificate Authority implementation is necessary to secure high assurance to the organization. The Root CA should be deployed along with HSM (Hardware Security Module), crucial for key security.
-
Making Use of Automation:
Automation helps to improve efficiency and decrease human error in PKI management. Human nature is to commit mistakes in various tasks such as keeping count of certificates and keys, tracking the expiration date, storage of keys, etc. This automation can be used to renew the certificates and keys. It can also be used to track and store data of the number of certificates, what they are, who requested them, the purpose of the certificate and access to them, etc.
-
Understanding the Requirement:
Many organizations commit the blunder of designing and deploying their Public Key Infrastructure without finding their requirements. It is indispensable to use an appropriate PKI design that is good for the organization.
Conclusion
Cybercrimes are getting developed along with technology. In this world of technology, it is essential to have a secured tool to secure your confidential and sensational data from cybercriminals. Public Key Infrastructure is a tested and proven security tool in Information Technology. The implication of PKI has expanded to secure more business infrastructure and applications, which is emerged as a cost-effective technology. So, it becomes essential to follow a best practice for the lifecycle management of Public Key Infrastructure.