An Insider Threat is a risk that can cause individuals with access to an organization’s systems, networks, or data to exploit that access for a malicious purpose.
This threat can be caused by employees, contractors, business associates, or anyone with authorized access to assets of the organization.
Organizational Security Best Practices for Insider Threat Detection and Prevention
Today, organizations are constantly facing growing threats and unfortunately within. Most of the time, this threat goes ignored, which causes a huge risk to the security and integrity of an organization’s crucial information.
Insider Threats pose a significant risk to the organizations, as they involve individuals within the organization who’ve authorized access to sensitive information. You may wonder how it happens? So, these individuals may intentionally or unintentionally cause harm to the organization’s security and integrity.
Even statistics also show that Insider Threat is the biggest threat to the organization. According to the 2023 Insider Threat Report by Cybersecurity Insiders, 74% of organizations face at least a moderate level of vulnerability to Insider Threats.
It is crucial for organizations to take safety measures to detect and prevent Insider Threats. In this blog, we will explore how to Identify and prevent Insider Threats to ensure the security of your organization’s valuable assets.
What is an Insider Threat?
An Insider Threat is a risk created by individuals who work within an organization and have the ability to access its computer systems, networks, or information.
These individuals may misuse their access to carry out harmful activities. Generally. The threat can arise from employees, contractors, third-party, business associates, or anyone who has authorized access to important organizational resources.
There are two main types of Insider Threats: unintentional and intentional. To break it down, unintentional threats are like negligence and accidental. At the same time, in intentional threats, they are like a malicious insider. Let’s understand them individually.
-
Unintentional Insider Threat
Negligent
In negligent Insider Threat, an insider generally exposes an organization to a threat through negligence. They are familiar with security and policies but become careless and create a risk to the organization.
Accidental
As the name suggests, this type of threat generally accidently causes an unintended risk to an organization.
-
Intentional Insider Threat
Malicious Insider Threats
This threat is also called an intentional threat. To be specific, a threat that intended to harm an organization for personal benefit or for a malicious intent.
There are other Insider Threats, too, like collusive and third-party threats. Now, let’s understand why Insider Threats are on the rise and what organizations do not know yet.
Why Insider Threats Are On the Rise
So far, we have seen that Insider Threats can be intentional or unintentional and cause huge harm to an organization’s value, financial stability, and intellectual assets. The following are the various factors why Insider Threats are on the rise:
-
Rising Dependency on Technology
As businesses increasingly rely on technology and the internet, they become more susceptible to Insider Threats. The digital storage of data facilitates easier access, theft, or misuse of sensitive information by insiders. In addition, technology-savvy employees can utilize digital tools to spoil the organization’s activities, further complicating detection and prevention efforts.
-
Negligence of Insider Threats
Organizations tend to prioritize external threats more than potential risks incurred by insiders. This underestimation creates an environment where insiders, particularly those with authorized access, can implement undetected malicious activities. The lack of rapid detection tools and procedures further amplifies the effectiveness of insider crimes.
-
Dissatisfied Employees
Employees dissatisfied with their jobs or employers are more inclined to participate in Insider Threats. Discontent of an employee can manifest in actions such as stealing information, damaging company assets, or engaging in activities detrimental to the organization.
-
Remote Work and the Impact of COVID-19
The pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote work policies, heightening the vulnerability to Insider Threats. Monitoring employee behaviour becomes more challenging in remote work settings that allow insiders to access confidential data or engage in malicious actions. The stress and uncertainty from the pandemic further lead to a surge in Insider Threats.
-
Insufficient Awareness and Training
Unintentional Insider Threats often arise from employees needing more awareness of security risks or a clear understanding of company policies. Cases such as sharing sensitive information or falling victim to phishing scams commonly happen with unaware employees. Regular and comprehensive security awareness training is imperative for preventing such security breaches.
Best Practices for Insider Threat Prevention
Here are some of the best practices you can follow to prevent Insider Threats.
-
Establish a Strong Security Culture
Build a strong security culture that includes the process of identifying and blocking misuse by insiders (who can be a threat). This should also indicate what are the consequences of Insider Threats and provide a guide to investigate the misuse.
How to do it?
- Organizations can set a clear security policy and guidelines
- Schedule a regular cybersecurity training and awareness programs for staff
-
Secure Data Handling
It is important that organizations keep an eye on their data and place access controls along with monitoring access. The reason is because it can help to secure lateral movements and protect useful information and intellectual property.
How to do it?
- Establish a strong password and implement multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Provide limited access to crucial data on a need-to-know basis
- Encrypt sensitive data to prevent data breach and attacks
-
Define and Detect Baseline Behavior
Try to identify any unusual activity happening in your organization’s LAN. Baseline behavior monitoring can help you identify and stop insiders. This is important for both individuals and network activities.
How to do it?
- Track network activities actively to establish a baseline
- Use anomaly detection tools to monitor any unusual patterns.
-
Run Periodic Risk Assessments
This is important because risk assessments can help you know your critical assets, their vulnerabilities and the threats. It is important for you to know various Insider Threats risks. Then, you have to see which risk is more damageable and that’s how you’ve to prioritize them.
How to do it?
- Look out for your crucial assets and their vulnerabilities
- Prioritize the risks based on their potential impact and areas of improvement.
-
Secure Your Infrastructure
It is important to limit who can get into critical infrastructure and sensitive information using the tight controls.
How to do it?
- Implement strong access controls and authentication mechanisms
- Review and update security measures daily to ensure they’re effective against evolving threats. This can be done using firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection, and monitoring tools.
The practices mentioned above collectively contribute to a robust Insider Threat prevention strategy. Therefore, implementing these practices can promote a secure environment and minimize the risk of malicious activities within the organization.
How to Detect Insider Threats?
Consider implementing the following best practices to detect potential Insider threats.
-
Detect Breached Accounts
At an early stage, it is important to catch unauthorized account access so that users can change their passwords and restore their compromised accounts. One way you can do this is by analyzing user behavior and detecting unusual patterns. By methods like phishing attacks, malicious actors gain access to accounts. So, it’s important to be vigilant and take safety measures to protect your accounts and information from such threats.
-
Track Third-Party Access
It is crucial to be careful about who you let access your system. This includes individuals who work for other companies that you might be working with. You cannot control how secure their systems are, but you can limit how much you trust them when they’re working in your system.
-
Speak Up If You Spot Anything Fishy
Keep your employees aware about potential threats that could happen to your organization. What employees can do? So, they can do so by keeping an eye out for any stranger behavior and letting the right people know. It is also crucial for employees to make sure they’re not accidentally causing any harm to themselves in terms of security.
-
Manual and Automated Audits
These audits can work like magic, and they are necessary for any organization to stay safe and protected. A manual audit involves the evaluation of systems, while an automated audit is done through any tools or technologies. There are various technologies available, such as User and entity behavior analytics, event management software, productivity software, and employee monitoring tools.
-
Perform Sentiment Analysis
Analyze the sentiments and intentions of individuals to gauge their emotional state and behavior. By conducting frequent assessments, you can detect if an employee is stressed, facing financial difficulties, or not performing well. When this information is combined with HR data and user access records, it can help you identify potential insider threats.
Top 5 Real-life Examples of Insider Threat
Let’s look at some real-life examples of Insider Threats of big enterprises.
-
Data Breach by SGMC Employees
In November 2021, a former South Georgia Medical Center employee based in Valdosta, Georgia, downloaded sensitive data onto a USB drive immediately after resigning.
As a result of this breach, patients’ confidential information, including test results, names, and birth dates, was exposed.
To mitigate potential harm, the medical center had to extend services such as free credit monitoring and identity restoration to affected patients.
The root cause of this Insider Threat is that a former employee exploited legitimate access privileges and faced no obstacles for unauthorized data downloads.
Fortunately, the medical centre’s security software promptly detected the breach, triggering an alert to cybersecurity personnel. The incident was filed and solved by Law enforcement and Lowndes County Sheriff’s Office as they promptly recovered files.
-
Data Breach in Mailchimp
Mailchimp and its affiliates faced several cyber threats throughout 2022. In January 2023, malicious actors executed a successful phishing attack, deceiving at least one Mailchimp employee into exposing their credentials.
This breach compromised a minimum of 133 Mailchimp user accounts, which impacted big businesses such as Statista, Yuga Labs, Solana Foundation, and WooCommerce.
The attack’s root cause was the social engineering tactics aimed at Mailchimp’s employees and contractors.
This breach was successful due to employees’ negligence or inability to recognize the social engineering scheme which grants unauthorized access to their accounts.
This incident emphasizes the significance of addressing employee-induced data breaches and the need for comprehensive cybersecurity training rather than relying solely on security software.
-
Tesla’s Employees Leaked PII Data to Foreign Media
In 2023, Tesla continued to face various faces of Insider Threats. During this period, Tesla encountered a significant data breach planned by two ex-employees.
These employees leaked highly sensitive personal information to a foreign media outlet, including names, addresses, phone numbers, employment records, and social security numbers of over 75,000 present and past employees.
This insider breach also exposed customer bank details, proprietary production information, and criticisms concerning Tesla’s Full Self-Driving feature.
Despite legal actions pursued against the former employees accountable for the data breach, the impact on the brand’s security reputation remained intact.
-
Twitter (Now X) Falls Trap to Social Engineering
In July 2020, cybercriminals implemented a phone-based spear-phishing strategy targeting Twitter (Now X) employees to compromise numerous high-profile accounts.
Initially, the attackers aimed to gather insights into internal systems and processes. As the campaign progressed, they identified suitable individuals to target, which led to gaining access to account support tools, which enabled the compromise of 130 Twitter accounts.
-
Poaching of Apple’s Trade Secrets
In April 2022, Apple initiated legal action against the secretive startup Rivos, asserting that the company was involved in a coordinated effort to attract Apple employees specializing in proprietary System-on-Chip (SoC) technology.
Rivos enlisted the services of 40 former Apple employees, which prompted Apple to accuse at least two engineers of absconding with gigabytes of confidential SoC data.
This information has the potential to accelerate the development of SoC at Rivos. In its legal documentation, Apple claims the stolen data is a multi-billion dollar theft, highlighting the high financial investment and over a decade of research dedicated to its SoC technology. This intellectual property is now in the possession of a competing entity.
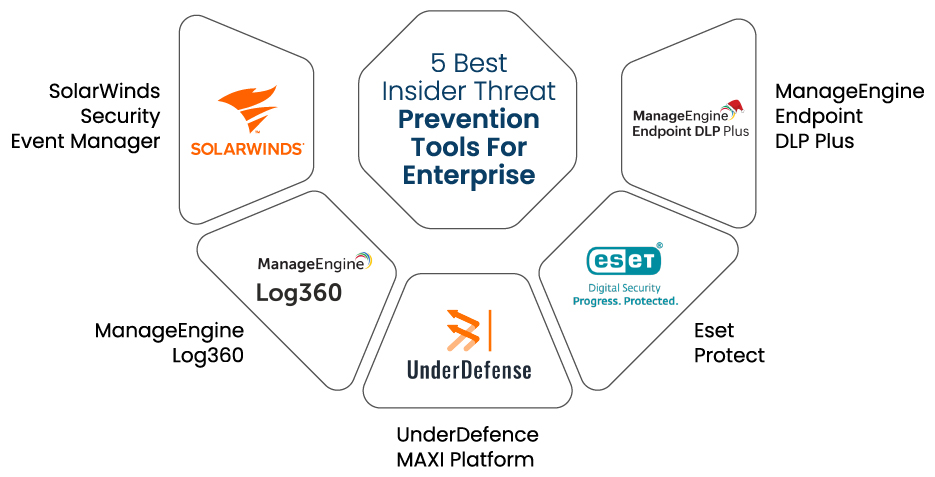
The Best Tools to Prevent Insider Threats for Enterprises
The following tools stand out as the best choices for preventing and mitigating Insider Threats:
-
SolarWinds Security Event Manager
SolarWinds Security Event Manager is a comprehensive software solution designed for security scanning of log messages. It includes a log manager that collects, consolidates, and organizes logs which enables easy access for viewing and manual analysis. The package of automated analysis service is specialized in detecting Insider Threats, intrusion attempts, and malware.
-
ManageEngine Log360
ManageEngine Log360 is a suite of security solutions focused on a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) framework. This system for detecting threats utilizes log files as its primary data source, and as part of its offering, includes a log manager.
The threat-hunting feature operates on anomaly-based principles utilizing User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) to detect regular behavioral patterns specific to user accounts and devices. Any deviation from the typical activity pattern, such as the sudden alteration in behaviour characteristic of Insider Threats, triggers alerts within the Log360 system.
-
UnderDefence MAXI Platform
The UnderDefense MAXI Platform offers a dedicated team of cybersecurity professionals to assist with the security software selected by organizations. It caters to businesses that don’t want to maintain an in-house security team.
Known as a service, not merely a package, the UnderDefense MAXI Platform grants users entry to a cybersecurity expert team. This team takes charge of monitoring the given security software by ensuring comprehensive surveillance. This service operates around the clock with scheduled shifts and provides continuous support 24/7 through the capability of accessing networks globally via the Internet.
-
Eset Protect
ESET Protect, a comprehensive cybersecurity solution uses a hybrid approach to threat detection utilizing both on-device components and a cloud-based coordinator.
This solution actively scans for various threats that encompass automated dangers such as malware and human-based risks, including intruders and intentional or unintentional insiders. Through its focus on identifying unusual activities, this solution increases security measures to ensure robust protection.
-
ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus
ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus includes Insider Threat detection through user activity monitoring specifically related to sensitive data access.
While numerous Insider Threat identification systems utilize AI-driven User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) for comprehensive user activity monitoring, the approach by the ManageEngine package is more streamlined as it focuses solely on file activity.
Functioning as a comprehensive data protection and compliance management solution, ManageEngine Endpoint DLP Plus not only facilitates user activity tracking but also excels in Insider Threat detection.
The system recognizes sensitive data and creates protective strategies to safeguard it. The primary risk to these data repositories usually arises from users with authorized accounts.
Conclusion
In today’s highly digitized and interconnected world, organizations must remain vigilant against Insider Threats that can compromise their security and reputation. By understanding the different types of Insider Threats, identifying warning signs, and implementing preventive measures, organizations can create a strong defense against internal risks.
Proactive efforts to educate employees, monitor network activities, and implement strict access controls are essential aspects of a comprehensive Insider Threat prevention strategy. By taking these steps, organizations can foster a secure and resilient environment and safeguard their most valuable assets from potential internal threats.