Understanding Data Security Governance – Role, Policies, and Framework Models
In this digital world of business, data plays a vital role, and these data are the assets of every organization. Improper governance of these data may lead to critical risks for the business. In this document, let us investigate data security governance, policies of data security governance, roles of data security governance, models of data security governance, and its best practices.
What is Data Security Governance?
Data Security Governance is the process of improving the value of the business by identifying the important data of the business and ensuring its greater level of quality. It is the set of processes, metrics, standards, policies, and roles that will ensure that the information is used effectively by enabling an organization to achieve its goal.
It will define the situation-based action maker on the required data, which includes the action method. Also, Data Security Governance will establish the responsibilities and processes to ensure the quality and security of the data used across the organization. A well-planned data framework and data strategy are important for an organization to work with its big data.
Policies of Data Security Governance
Data Security Governance policy is a bunch of guidelines used to make sure that the assets of data are correctly used and managed. It has a committee responsible for ensuring the quality and accuracy of data and protecting the data by clarifying the standards, principles, and regular practices. The common areas governed by Data Security Governance policies are as follows.
- Availability of data
- Usability of data
- Quality of data
- Integrity of data
- Security of data
Availability of Data
Availability of data is essential to ensure that the available information is accessible, accurate and easy to read by the users. The organization requires data to develop the business and its performance, which leads to financial loss and reputation damage. Hence, this can be accomplished by improving the physical infrastructure of the organization (disks and servers, which provides easy access to the data), increasing recovery time (reboot, troubleshoot, and replacement of hardware), removing unwanted/defected data (incomplete data, wrong data, expired data should be removed), formatting well-organized data (formatted data is easily available and can reform accordingly). Various tools can also be used to maintain the Availability of Data.
Usability of Data
Data usability enables the user to acquire useful information from the given database. And checks whether the information is structured, neatly labelled, and documented to be compatible with the user.
Quality of Data
Quality of data is the important factor in a data governance policy which helps to reach the organization standards. Here every organization needs high-quality data to take a critical decision, which helps grade up their reputation. Quality of data completely relies on the consistency, accuracy, uniqueness, and timeline of the data, which refers to the techniques or activities used by the suitable data.
Integrity of Data
The integrity of the data is the one that makes sure that the data is safe and secured throughout its process. It mainly focuses on the accuracy, validity, and readability of the data in the given database. If data integrity is secured, the data with the database will stay accurate and readable even if it is not used or used frequently.
There are a few important types under Integrity of Data
- Entity integrity of Data
- Domain integrity of Data
- Referential integrity of Data
- User defined integrity of Data
Entity Integrity of Data
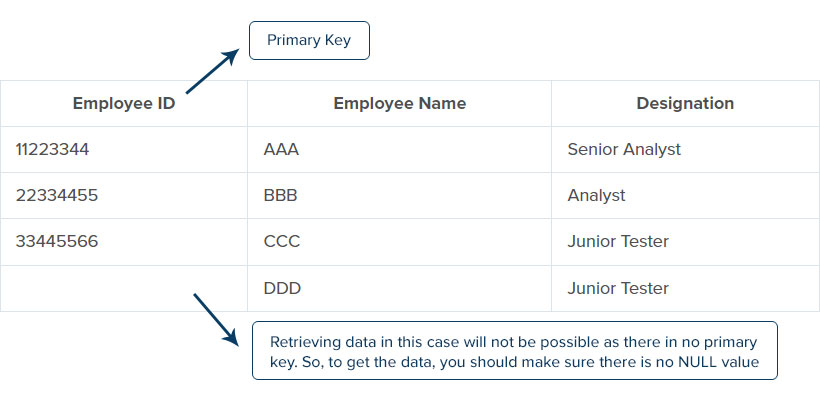
Entity integrity is the one that has a unique key at each row of an entity; here, the key may be either row or a combination of rows with unique and non-null values. If the entity in the row is the same, i.e., two or more entities with the same identity, there will be a chance of getting confused. So, to avoid this, we should make sure each row in the table consists unique key. Entity integrity is important in the database because it gives accurate results for every search in a specific row.
For example, let us consider the employee ID, employee name, and designation database. Here we can see the two employees with the same name and designation. If we retrieve the data with the employee’s name or designation, it shows both the employee row, which will be confusing and difficult to retrieve the data. So, to solve this problem, we should use the primary key at each row by giving a unique identity for every entry at the table and ensuring that there is no null value.
Domain Integrity of Data
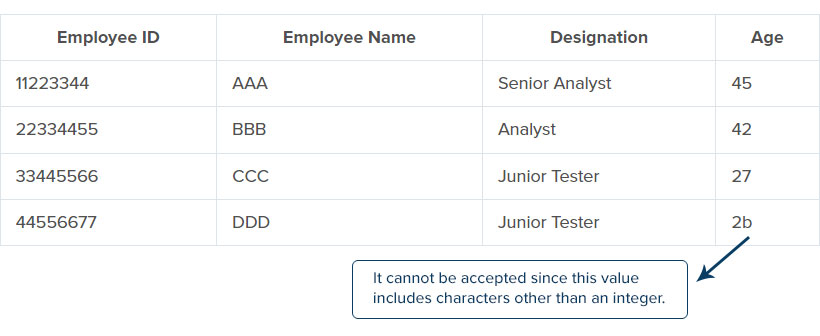
Every column in the table should be in a defined domain. Domain integrity includes various rules and ensures that the entire database contains valid values. It is restricted to the type, format, and quantity of the data stored in the database. Data type in the table can be a decimal, character, or integer; then, the database must contain any type of data within the given data type.
For example, let us consider the table with an employee ID, employee name, employee designation, and age. Here we can see that the table’s constraints are of the same data type except for the age column. So, in case of any entry of an extra character in the data type, that data will not be acceptable and shows an error.
Referential Integrity of Data
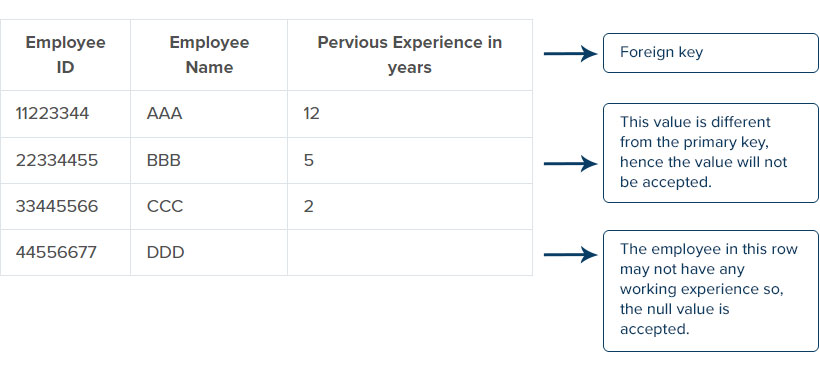
Referential Integrity is in which the foreign key is logically dependent on the primary key. It refers to the relationship between two tables, the Integrity which consists in one table should contain in the other table. Referential Integrity is also a method of checking for the accuracy of the data within the given database. Some standard rules are made to structure the database, which involves using the foreign key and ensuring that the addition or changes in the database are the same as the data integrity. Referential Integrity consists of a foreign key and ensures that it contains the primary key, or it can also be the null value.
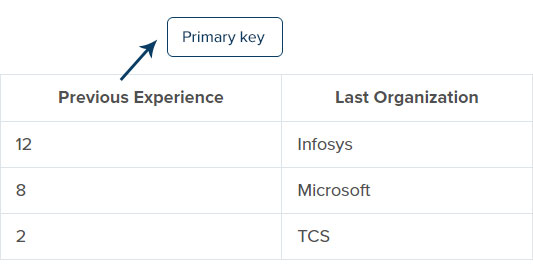
For example, consider two tables, the foreign key table with – employee ID, employee name, previous experience, and the primary key table with – previous experience, last organization. Here we should make sure that the foreign key table’s data should also consist of the primary key table, and it can also be the null value. The value will not be accepted if any values in the previous experience column (foreign key) is not present or changed in the previous experience column (primary key).
Primary key table:
User Defined Integrity of Data
User-defined integrity consists of certain constraints and defines business rules, which are used to fulfil the user’s required needs and ensure that it does not fall into another integrity category. In some cases, the other integrity, such as domain integrity, entity integrity, and referential integrity, will not have enough capacity to maintain or safeguard the data; in such cases, User-Defined Integrity Data is used.
For example, let us consider a table with – employee ID, employee name, designation, and serial code. The serial code has specific constraints, following an integer after the ESC character. So, if a character or integer is missing in any row, then the integrity will not be accepted.
Security of Data
Security of data is the one that the organization uses to ensure what type of data is used, where the data is located, how to access the data and the availability. Data security is used at different levels in the organization to help in optimizing the data to be safe and secured. Protecting data is an important aspect since any misled data or loss of data affects the organization’s reputation. It may lead to financial loss and is subjected to penalties.
Roles of Data Security Governance
Roles of Data Security Governance are usually performed by the organization’s group members and are responsible for assigning work, monitoring, reviewing, managing, etc.
There are standard Roles of Data Security Governance implemented in the organization. These roles include data steward, Chief Data Officer, Owner of the Data, Editor of Data, Documentation Manager of Data, Expert of Data, and Quality Manager of Data.
Role 1: Data Steward
A data steward is a member of the organization. He is responsible for handling the process and policies of the data and ensuring that the data is accurate, well-formatted, and of high quality. Steward is the one who has the wider experience and is expertise in both business and IT database. Data steward involves Data producers and Data users. The data producers manage the data by updating, producing, retiring, achieving, deleting, and creating the data. And data users maintain the integrity of the data by performing their given work.
There are different types of data steward role; some of them are as follow,
- Business Data Steward
- Technical Data Steward
- Data Governance specialist
- Chief Data Steward
- Subject Area Data Steward
- Executive Sponsor
- Program Manager
- Owner of the Data
- Custodian Data
Business Data Steward
Business Data Steward is the expertise and has strong knowledge in the business function. The data steward works with the business and owns the data, which is used to define the plan’s objective. Business data has major responsibilities like managing the critical data in transactional and reference, which the business function performs.
Technical Data Steward
Technical Data Steward has enough knowledge in IT functions that understands and works according to the needs of the technology. The responsibility of the technical data steward includes considerations and key characteristics to understand how the data is stored, created, transformed, and manipulated in the technical system.
Data Governance Specialist
Data Governance specialist includes the responsibility of implementing certain processes and policies and ensuring that the data’s administrative management and operation are up to date.
The Data Governance Specialist performs some important roles, such as developing data rules, policies, and standards followed by the organization. It is also used to grow the organization’s key characteristics such as communication plan, meeting notes, socialization plan in the data governance, domain model, etc.
Chief Data Steward
Chief Steward is responsible for maintaining the complete stewardship program and management for a particular area. Chief Steward is also called as leader of the stewardship in many organizations and is elected from the domain data steward. They provide an analytical strategy and outline the data by defining it across the organization.
Subject Area Data Steward
Subject Area Steward is the person with logical knowledge used to consider the domain or subject area of the data. The data governance council designs the subject area steward, and the policy identifies it; the policy in most organizations involves data classification, data privacy, and data operation.
Executive Data Sponsor
Executive Data Sponsor is a role of data governance in an organization responsible for checking whether the organization’s data is well fitted and ensures the quality of the data. Executive Sponsor chooses the best among the group to ensure whether the organization follow the rules, standards, and privacy policy.
Executive Data Sponsor includes some characteristics like good communication skills, knowledge in corporate assets, trustworthiness, challenging mindset, executive grading, and someone who wants to be an executive sponsor.
Program manager
A program manager is an experienced person with a high level of knowledge in the organization’s technical and business functions. A program manager is responsible for monitoring the day-to-day work, budget, project plan, project scope, goal of the organization, organizations standard, and schedule. Program Managers also are responsible for assigning the work by ensuring which data is stored, shared, cleaned, collected, protected, and utilized.
Program managers maintain their contacts in the organization and successfully achieve their goals through interpersonal skills like strong communication and leadership qualities.
Owner of the Data
The Owner of Data can either be a team or an individual, depending on the enterprise and the data type. Owners are responsible for deciding by selecting the right person who can access the data, how to use it, and edit the data.
The role of Data Owner and Data Steward may be different from each other, but both are involved in the same activities.
The owner’s responsibility varies from a different organization, which includes security of the data, oversight of the data management, quality of the data, managing data policies, and managing the risk in the organization.
Custodian Data
The responsibility of custodian data is to make sure that the data is equally distributed between the technical and business department. Also, it should ensure that the data meets the given guidelines and standards at each stage of the development process within the organization.
Role 2: Chief Data Officer
Chief Data Officer is the senior official in the organization responsible for supervising the data governance program. The responsibilities include development of the policy, strategy in the given information, approval of the project, hiring staff, funds for the program, and leading progress of the program.
Role 3: Owner of the Data
The data owner may be an individual or a partner who differs from each organization. The responsibility performed by the owner is to make sure that the data in the domain is distributed across the business line and to the entire enterprise.
Owners are not voting members in the organization but are operating committees. Also, owners are involved in defining the data, checking for the accuracy and quality of data across the organization, and approvers the list of data that contains a brief explanation.
The data owner rectifies the error and gets a solution by working with the various owners and providing input to the operating committee by establishing the regulatory requirements, policies, and solutions to the software used in the organization.
Role 4: Editor of the Data
Editor’s responsibility includes editing the data, creating the file, and maintaining the data established by the data definition and similarly works for the data content for a given area. Editing data helps to detect the error, review for consistency of the data, find the solution and corrects the mistakes. It also provides adequate and accurate information and improves the quality of data.
Role 5: Documentation Manager of Data
The responsibility of the Documentation Manager includes directing the project, developing the standard methods to prepare the document, and frames roles and responsibility of the data governance. The documentation manager usually helps improve the quality of projects and provides proper guidance to the steward data.
Role 6: Expert of Data
Experts are those who know the business functions and information technology. Here the expert of data gives the training to editors on data definition, including collecting the required data and making sure they can create and maintain the data accurately.
Role 7: Quality Manager of Data
The quality manager provides various methods to establish accuracy and high-quality data. It also supervises the working process to ensure that the given database meets its standard. The responsibilities of the Quality Manager include checking the performance and reporting the data by measuring its standards and developing the quality by inspecting the data.
Models of Data Security Governance
There are different varieties of Models in Data Governance that are leveraged in the developed business. It provides the structure of how the data is created, how it is maintained, where it is stored, and how to destroy it. A single model of data governance fits all the organization, but there are also various models of data governance that can be used within the organization.
The most used Models of Data Security Governance are as follow,
Centralised – Single or Multiple Business Unit Data Governance Model:
The centralized Data Governance Model is used to determine how the data is governed in the organization. This model can be characterized by a single business unit or multiple business units depending on the master data is centralized. Here, the organization sets up a master data model used by the consumers or business unit to manage their data within the central body.
This model is well suited for medium and large organizations, and it supports the master data for a longer span of life. The centralized model provides master data to other business units and a longer life cycle with vendors and customers.
Centralised and Decentralised executive – Data Governance Model:
Here, the Centralized Data Governance Model is used to establish the policies and framework of the data governance. In contrast, Decentralized Data Governance Model creates the individual business units and maintains the part of master data.
The organization uses automated tools at the source, which prevents de-duplicate data, which helps in leveraging the organization model effectively. It also provides controls and fixes the inconsistency of the data by auditing.
De-centralised – Single Business Unit Data Governance Model:
Here, the Decentralized is characterized by the individual business unit. The master data is maintained, used, created, and managed by the individual business user. This model is best suited for small organizations and provides simple data maintenance. The lifecycle of the master data is short, and it does not share the master data with any other business unit.
Single Business Unit Decentralizes some tactics to ensure that the model works effectively, which provides the experts and clearly defines the ownership within the organization.
De-centralised – Multiple Business Unit Data Governance Model:
This model has Multiple Business Units maintaining the master data and works with vendors, customers, materials, and other interests. Decentralized Business Unit Model is best suited for small and medium organizations, and it offers simple data to maintain. Another business unit can use the master data offered in this organization, and it provides a shorter lifecycle to the master data.
Here, the automated tool used to ensure that the data is in proper consistency is independent of the master data and the creator of the data.
Best Practices of Data Security Governance
Data Security Governance is a system that controls the entire data assets, who has the authority to access the data, and how to use it. Data governance initiative must begin with the support of stakeholders and management in which the data is managed and owned. Usually, the best way of initiating the project is to start with a small pilot project, and a set of data is tested. A pilot project is used to demonstrate the business objectives and effect of data governance activities.
Data governance tools are used to evaluate and standardize the data in the organization, and it uses models, templates, and uses the tools which are currently booming. Using these criteria helps save time and develops the organization’s role by improving the integrity, quality, and accessibility of the master data.
Conclusion
The Data Security Governance helps us to understand the type of data used in the organization, and it carefully examines the data and manages it by identifying the errors and resolves it by introducing the perfect solution, which if not leads to the risk of losing the reputation and vulnerability of the enterprise. And it ensures that the provided data is protected, accurate, decreases the cost of data management, and meets the organization’s standard.
Data governance provides the best business outcomes and gives accurate results in the enterprise. Various Roles are used in the data governance system, which is the important factor in the organization used from starter to the expert who helps in operating the company. Data security governance uses some privacy regulations and creates rules that will be the key component in the organization’s development.