How AWS Integrates Security, Identity, and Compliance into its Cloud Infrastructure?
As more and more businesses adopt cloud computing services for their operations, the threat against cloud infrastructure is also increasing. AWS, the huge cloud service provider in the market, provides many security features to secure the cloud structure and customer data. It is essential to understand the service provider’s security policy before adopting it for the business. This document covers the topic of AWS cloud computing, working of AWS, AWS security, Identity and compliance, and AWS security best practices which provide more insight into AWS.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is an IT infrastructure that provides all computing services over the internet. It eliminates the need to install and maintain the physical data centres and servers on the company premises. The key feature of cloud computing is that it allows for scaling the resource that reduces the company’s financial burden. The computing services include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, security, and intelligence.
What is AWS?
AWS is the acronym for Amazon Web Services provided by Amazon.com. It is an IT infrastructure platform that provides cloud computing services through physical data centres spread across various locations. The AWS platform encompasses three cloud computing models, which are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and software as a Service (SaaS). The AWS offers cloud services to the organizations with pay-as-you-go options, thus eliminating the cost of infrastructure development and maintenance on the company’s premises.
How Does AWS Work?
The working of AWS is like the working of the operating system (OS) in the computers. For example, the operating system in the computer facilitates the users with various services such as e-mail, data storage, and other computing tasks. AWS like the operating system for thousands of computers, providing all the computing features such as communication, storage, security, and networking. In short, the organization’s computers will access all the AWS computing services through the internet. Therefore, the organization devices will have enormous computing power and storage and the latest software development and maintenance tools. All services will be available in the cloud platform, from which the organizations can opt for suitable services based on their requirements.
The AWS supports advanced technologies such as Virtual Reality (VR), Machine Learning (AI), quantum computing, Augmented Reality (AR), and other developing technologies. Many popular organizations have opted for the AWS services for their functions and business development.
AWS Services
-
Storage and Backup
One of the main reasons for opting for cloud infrastructure is that it provides huge storage facilities with easy accessibility. You can use this facility for various purposes like storage and file indexing. Business applications can also use this storage to handle the bulk data. The organization’s data backup is stored in multiple locations so that if one data centre fails, it can use the other to retrieve the data.
-
IT Infrastructure
AWS provides all the necessary IT infrastructure for the organization. It works based on the concept of paying for what you use. In this method, the organizations can pay only for the IT services. It comes with features like large storage, scalability, and flexibility in cloud services, which saves much money.
-
Social Networking
For the success of any business, digital marketing plays a critical role. AWS makes it easier through its social networking sites and engines. One can use it to communicate with the company’s stakeholders and customers. It also provides tools and techniques to develop social networking sites and helps to maintain them.
-
Mobile Applications
AWS provides all the services involved in the mobile application development cycle, such as analysis, development, testing, implementation, maintenance, and regular updates. It also provides additional features like database auto-scaling that improves the application performance.
-
Websites
The website hosting services are also included in the AWS cloud computing. Customers can choose from various options to develop and maintain their websites. Features like SSD- storage, secured data transfer, and DNS management helps the clients to maintain their sites easily.
-
Content Delivery and Media Distribution
AWS provides faster content delivery through its efficient content delivery network (CDN) called cloud front. It uses multiple servers distributed over different geographical locations to facilitate faster internet content. Media distribution is very much useful in streaming live and on-demand videos.
-
Search Engines
The AWS features like Cloud Search Elastic Search provide search engine solutions to set up, manage and scale the websites or applications. They are cost-effective and low latency search solutions.
-
Development and Test Environment
The organizations can easily develop and test their applications in the AWS development and testing features. It provides a perfect cloud platform to develop the application and test it in a real-time environment, including tools and software required for this process. One can access the cloud platform through the internet.
-
Academic Computing
The AWS proves to be highly efficient in supporting the research labs and institutions for the latest scientific research and technological development, Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and quantum computing for data storage, analysis, and communication.
-
Big Data
The big data features facilitated by the AWS cloud computing help organizations handle large data with ease. It also has scale-in and scale-out options that support unexpected data surges or reductions. The companies can store and manage the big data with efficiency and flexibility.
What is AWS Security?
The AWS cloud services come along with the security infrastructure to protect the cloud infrastructure and the customer’s data. With most companies adopting cloud computing for their business, the need for cloud security has also increased. Thus, AWS implements cloud security by using the shared responsibility model.
AWS Shared Responsibility Model
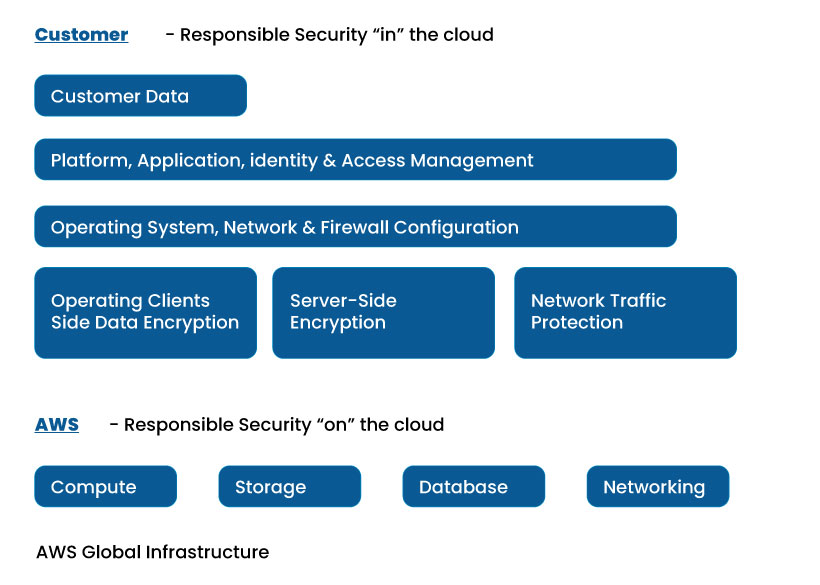
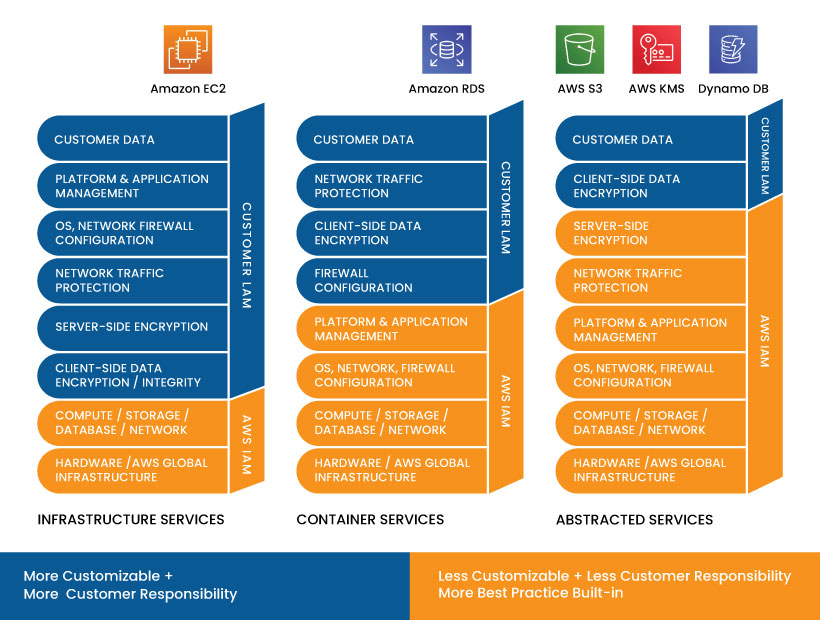
Securing the cloud platform is shared between the AWS and the customer in this model. The AWS is responsible for its Infrastructure, while the customers are responsible for their data and application. In other words, AWS takes care of its cloud platform, whereas the companies should take care of their belongings on the platform. The AWS cloud infrastructure involves hardware, software, networking, and facilities. Organizations must establish the necessary setup to secure their data and software, depending on the cloud service they adopt.
The responsibility is shared based on the level of abstraction from the customer. The higher the customer’s cloud services, the higher the cloud service provider’s responsibility. I.e., the customer can avail of any of the three services, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, from the AWS cloud provider. The responsibility of AWS depends on the level of service utilized by the customer.
The shared responsibility model helps to demarcate the boundary between the cloud provider and the customer. As the responsibilities of the stakeholders are predefined, it becomes easy to implement the security framework. It eliminates the rise of security blind spots due to confusion in sharing the responsibility.
The above image represents the share of responsibility between the AWS cloud provider and the customer, based on the type of cloud service chosen by the customer.
AWS Security, Identity, And Compliance
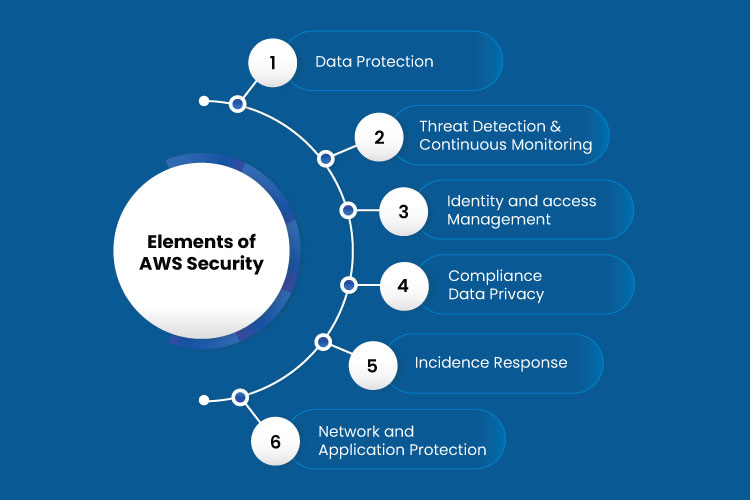
The AWS provides various products that help customize the cloud services to the customers. AWS provides cloud security, including data protection, Identity and access management, and other services. It is otherwise known as AWS security, Identity, and compliance and comprises all security frameworks provided by AWS.
Various tools and services are enveloped in the AWS security from which the customers can make use of the suitable service according to their business needs. Some of the components that form the part of AWS security are,
Data Protection
The goal of AWS security is to secure the data from unauthorized access. It is an important factor to provide data protection to gain the customer’s trust. For this reason, the AWS cloud provides various tools and services to secure customer data. The AWS security features like data encryption, key management, threat detection, and network firewall help customers protect their data.
Threat Detection and Monitoring
The AWS tools can monitor the client’s cloud network to detect any threat in the early stage. It helps to find and mitigate the threat before affecting the business. As the threats are detected in the initial stage, they can be eliminated, saving time and money.
Identity and Access Control
AWS provides the customer with control over their resources and cloud applications by utilizing the Identity and access control. With this feature, the customers can secure their data and resources by limiting cloud data or application access. Organizations can monitor their employees by defining their roles and login accounts. The AWS also supports Multi-factor Authentication to avoid illegal access to the cloud resources preventing data leaks or theft.
Security Compliance
AWS provides better compliance status by utilizing automated compliance checks. It makes sure that customer compliance harmonizes with the AWS best practices and the Industrial standard on which the company works.
Incident Response
AWS has a well-defined incident response plan back by the security experts. This setup helps to respond to any cyber threat as quickly as possible. It helps to secure the cloud platform from severe security breaches.
Network Security
The network-level security can prevent threats from external cyber attackers. One can do it by securing the network control points of the organization. AWS also provides tools to inspect and filter the network traffic to avoid illegal access to the cloud platform’s host, network, or application.
| Security Components | AWS Service |
|---|---|
| Identity and access management | AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) |
| AWS single Sign-on | |
| Amazon Cognito | |
| AWS Directory Service | |
| AWS Resource Access Manager | |
| AWS Organizations | |
| Detection | AWS Security Hub |
| Amazon GuardDuty | |
| Amazon Inspector | |
| AWS Config | |
| AWS CloudTrail | |
| AWS IoT Device Defender | |
| Infrastructure protection | AWS Network Firewall |
| AWS Shield | |
| AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF) | |
| AWS Firewall Manager | |
| Data protection | AWS Key Management Service (KMS) |
| Amazon Macie | |
| AWS CloudHSM | |
| AWS Certificate Manager | |
| AWS Secrets Manager | |
| Incidence response | Amazon Detective |
| Cloud Endure Disaster Recovery | |
| compliance | AWS Audit Manager |
| AWS Artifact |
Thus, AWS security, Identity, and compliance include various tools and services that provide the customers with solutions for cloud security. Some of the important AWS security services are discussed below.
AWS Security Services
Amazon Guard Duty
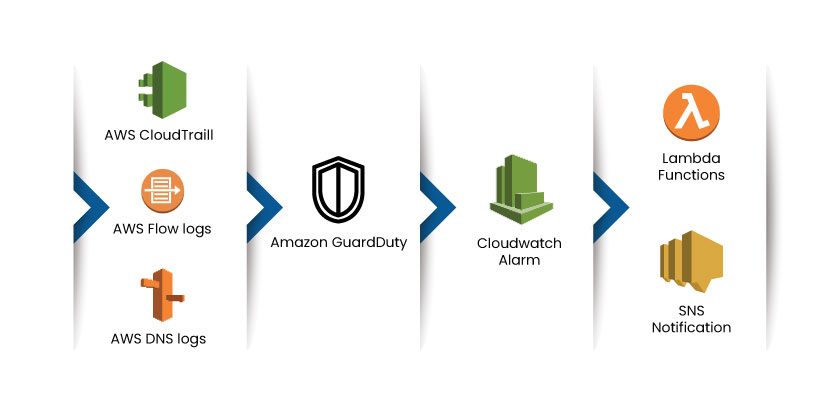
The Amazon Guard Duty is used to secure the AWS accounts, network, data storage, and workloads in the AWS cloud server. It uses automation and integrated threat detection techniques to monitor suspicious activities in the cloud platform. The organizations can tap Data sources such as AWS CloudTrail Event Logs, Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Flow Logs, and Domain Name System (DNS) to analyse the user activities and detect threats. The Amazon Guard Duty can identify threats like odd API calls, misconfiguration, port scanning, and DoS attack while sending threat alerts through AWS CloudWatch alarms. It also utilizes the AWS lambda functions to mitigate the threat.
The Amazon Guard Duty replaces the need for separate Infrastructure to monitor and secure the cloud server. It comes at an affordable cost, enabling security without affecting the current cloud workloads or applications. A few clicks can easily enable the Guard Duty in the Amazon Console.
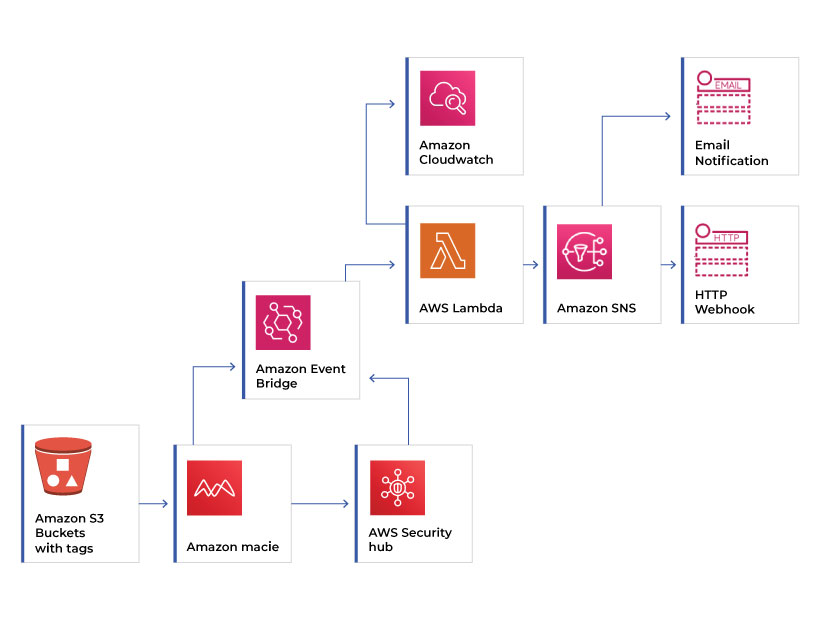
Amazon Macie
Amazon Macie is more of a security feature used to protect the objects in the Amazon S3 buckets. As a first step, it classifies the data in the S3 bucket based on the importance and privacy of the data. It categorizes the data like Personal Identifiable Information (PII), Protected Health Information (PHI) and Intellectual Property as highly confidential and protects it through security services and access control.
The functions of Amazon Macie include data classification in S3 buckets, identifying data location, data sharing (public or private), security, and compliance. There are three main features in Macie that helps to secure sensitive data.
- Macie summary dashboard gives an overview of the data classification in the S3 buckets. It also displays data access and movement information, either inside or outside the AWS account. Other particulars such as S3 storage consumption and data encryption status are also visible in the dashboard.
- The Macie jobs identify the sensitive data in the S3 buckets and report it automatically. It can customize it for either a one-time analysis or regular analysis.
- Macie’s findings include two reports on sensitive data and their security compliance. It helps the organization identify sensitive data and check its regulatory status to avoid security breaches.
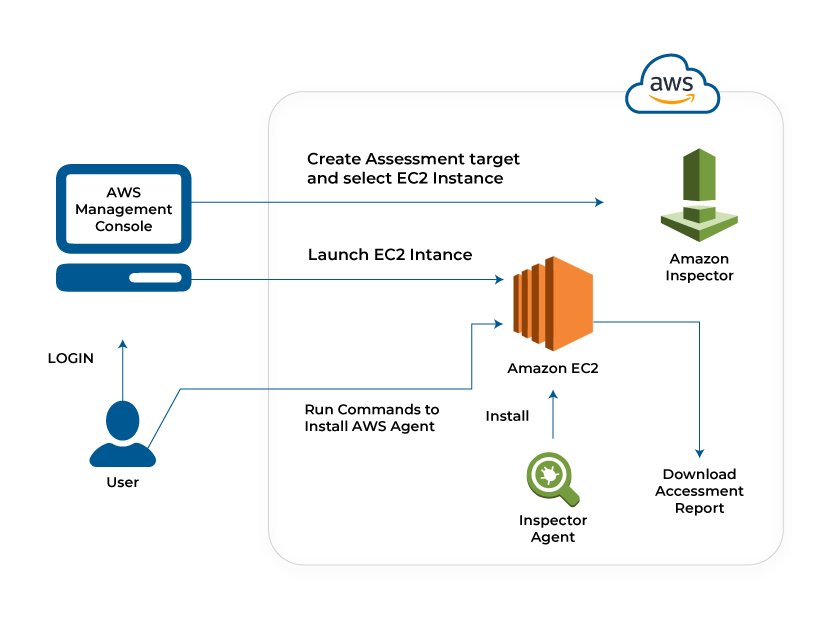
Amazon Inspector
The Amazon inspector is also used as a vulnerability detector whose function is like the Amazon Guard Duty. But there is a major difference between both the features. While the Amazon Guard Duty is used for monitoring the entire AWS cloud account, the Amazon Inspector specifically targets the cloud applications and website network to identify the vulnerabilities. It automatically detects the vulnerable spots by adhering to security compliance and best practices. The Amazon Inspector is highly utilized in the EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) instance for vulnerability management.
The AWS administrator can define the security compliance to be followed during the vulnerability assessment. Then the AWS inspector would send the findings through Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service). It can also be integrated as a security feature during the development of the cloud application and website software.
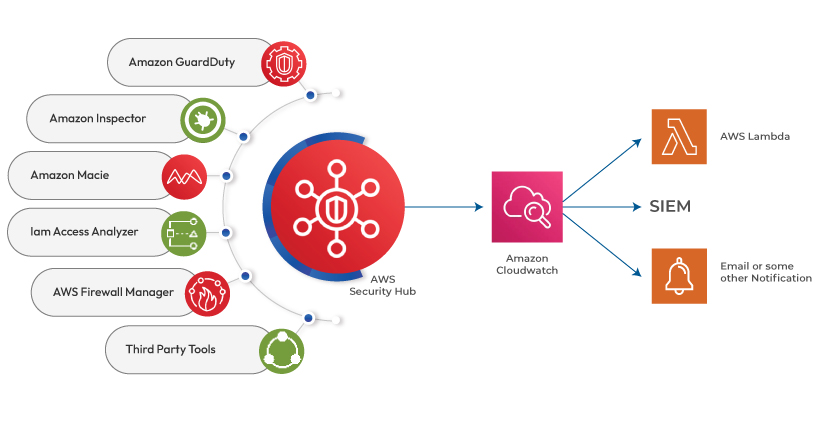
AWS Security Hub
As the name implies, the AWS security hub acts as a pivot for all security solutions in the AWS cloud platform. It gathers all the security findings from various AWS services to classify and prioritize the threat. After which, it automates the threat response by sending the findings through ticketing or SIEM (Security Information and Incident Management) tools. The security hub also scans the AWS account for misconfigurations, single or multi-account security checks, and AWS security compliance.
It helps the users organize the security alerts and prioritize the remediation process, which improves cloud security. The security hub integrates the information from several AWS services like Amazon Guard Duty, Amazon Inspector, Amazon Macie, and AWS Firewall Manager. It also supports third-party security products.
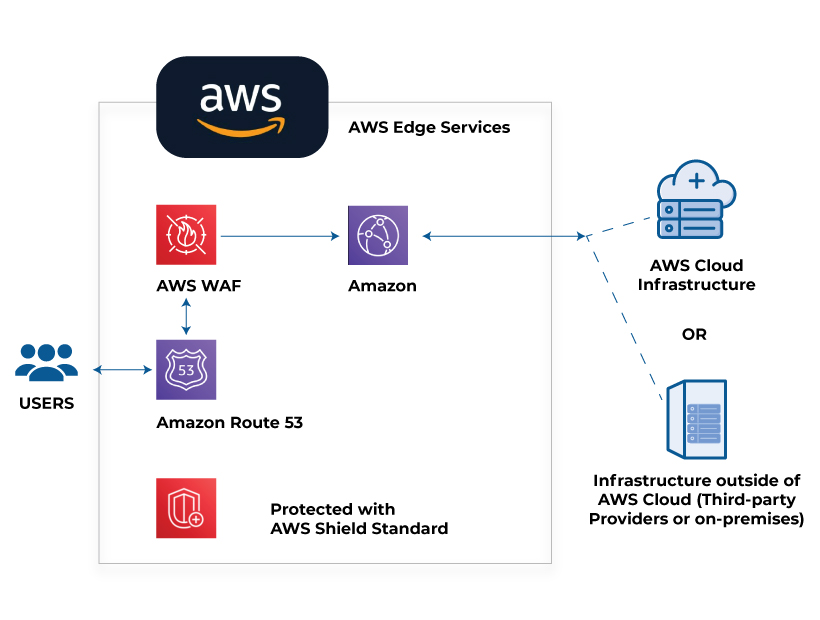
AWS Shield
As the name implies, the AWS shield is used as a guard against the Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. It is available as a default feature and the AWS cloud services, making it easy to implement without changing the cloud infrastructure. The major difference between the AWS Shield and the AWS web application firewall (WAF) is that the shield protects the entire cloud infrastructure (network and transport layers). In contrast, the WAF only protects the AWS applications (application layer). The AWS Shield can be implemented in two stages, with basic and advanced features. The basic level is free of cost, and the advanced level comes with additional charges. The AWS Shield protects against DDoS attacks through advanced detection and mitigation techniques.
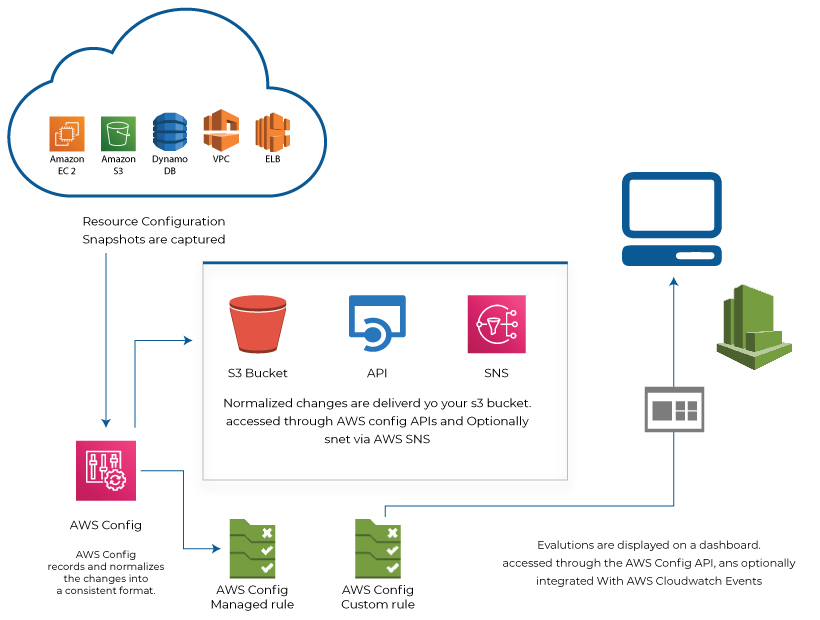
AWS Config
Resource management plays a crucial role in the success of any business. AWS provides cost-effective options like resource scalability to use the resource based on the requirements. But it becomes a hectic task to manage these dynamic resources. The AWS config service comes in handy to manage the AWS resources.
It analyses and evaluates the configurations of the resources to identify any vulnerable nodes. A person can use the AWS config to
- Scrutinize the configuration of the resources.
- Map the relation between the AWS resources.
- Cross-check the present configuration with the statutory configuration.
- Assess and report the changes made in the resources.
- Check the resource configuration with the regulatory compliance of the company.
In simple words, the AWS config provides a detailed view of the resources deployed by the organization. It helps the company to improve its productivity with minimal resources available.
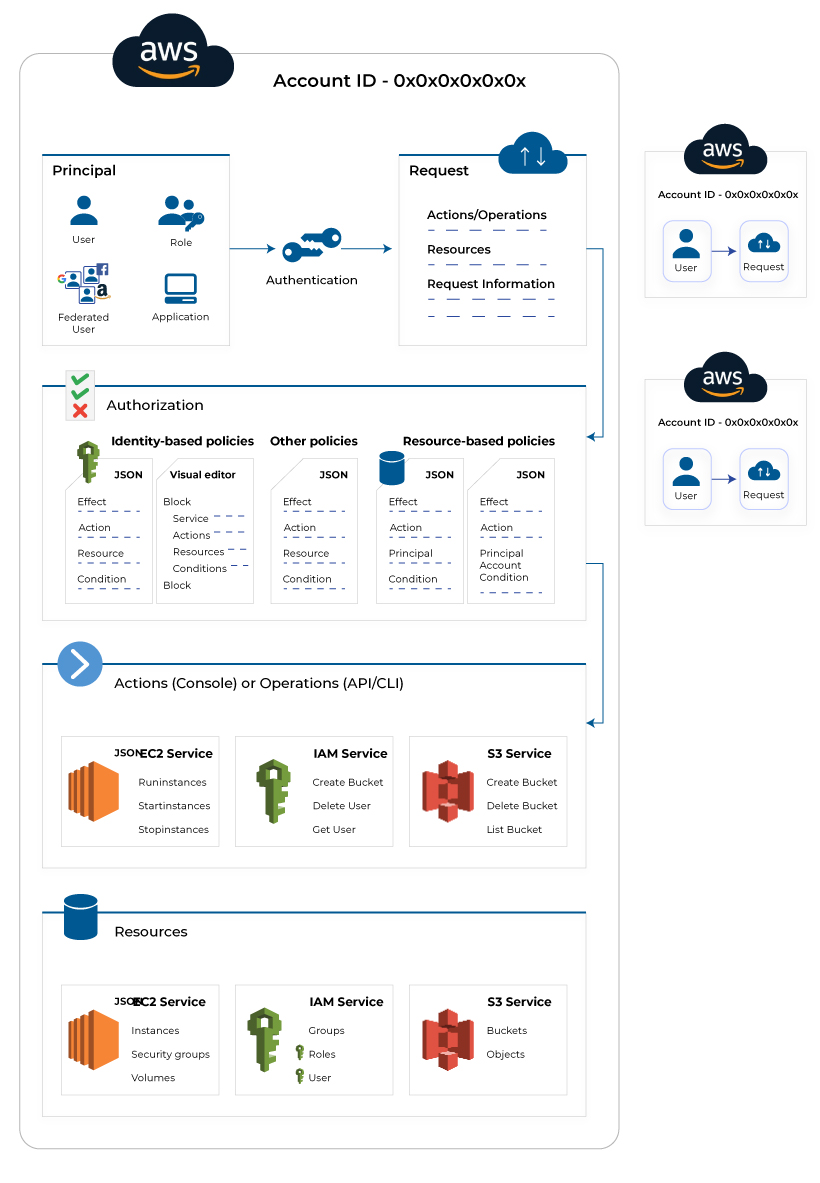
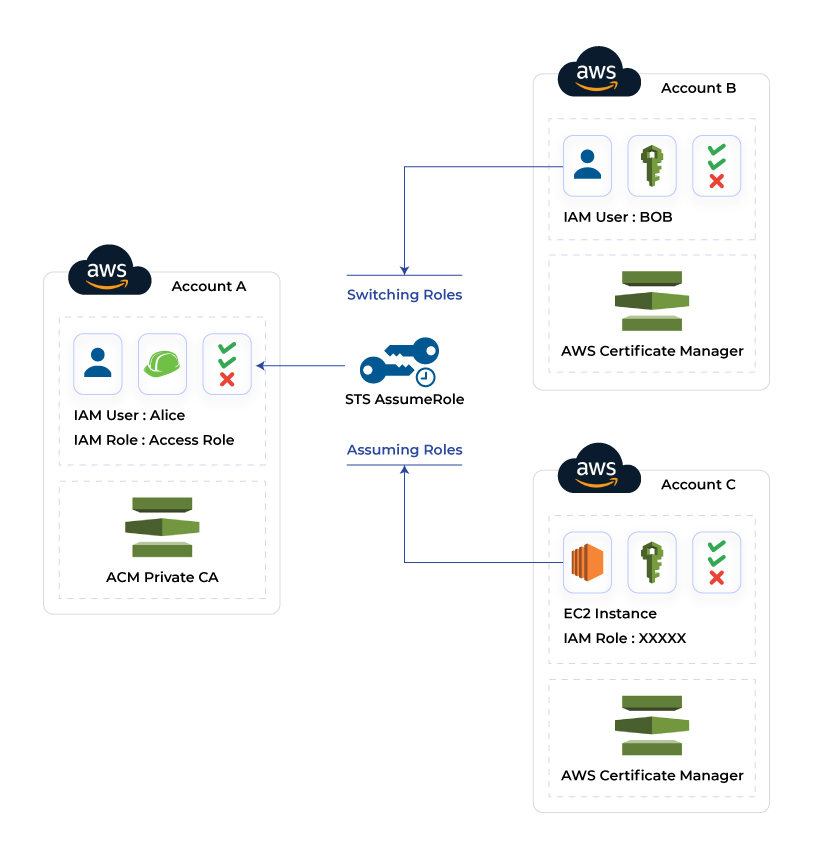
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
The Identity and Access Management is used to secure the whole AWS account through controlled access to the resources. It works on major concepts like the principle of least privilege and limited access permission. The IAM takes care of both users as well as resource control. The AWS users can be granted access through authentication, while the level of access to the cloud server is granted through Authorization. Therefore, IAM makes sure that the resources are accessed by the right users with the right permissions and roles.
The above image explains the working of the IAM, where access is granted to the employees based on their designation and work needs. The AWS account credential and defined permission are two important security components in the IAM. It also facilitates multiple users in a single AWS account. Each user is granted access to the different levels of resources based on their roles, also known as fine-grained permissions. Each user has a different credential to access the single AWS account.
Amazon Cloud Directory
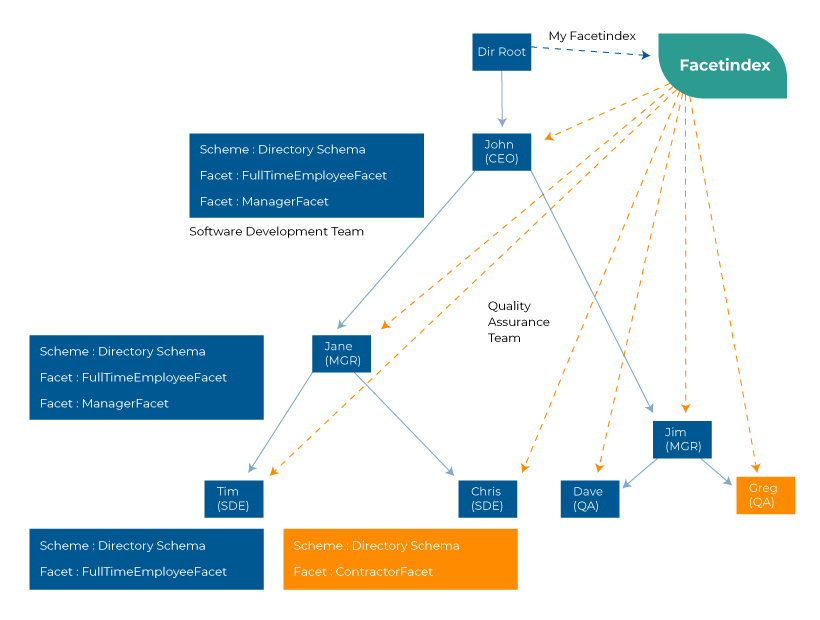
The main purpose of the Amazon cloud directory is to facilitate customized cloud directories with scalable objects and multi-dimensional hierarchies. A well-defined plan becomes an easy task to create object hierarchies with different attributes and facets. The advantage of this cloud directory is that it allows connecting any objects from different hierarchies. It is done through additional objects like indexes and type links. The cloud directory APIs can use path queries or unique object identifiers to navigate the objects. While the traditional directories provide single hierarchies for organizational structure, the Amazon cloud directory provides multiple hierarchies within a single structure. The use case of the cloud directory includes organizational charts and courses.
The above image explains the working of the Amazon cloud directory with an example. It represents an organizational structure with multiple hierarchies. The root is attributed to the CEO, whom manager-level employees follow. Here, the objects are split into two hierarchies: the software and quality teams. Each team has its group of employees in the succeeding hierarchy. In this way, multiple hierarchies can be added to the single organizational structure to be navigated through APIs.
AWS Secrets Manager
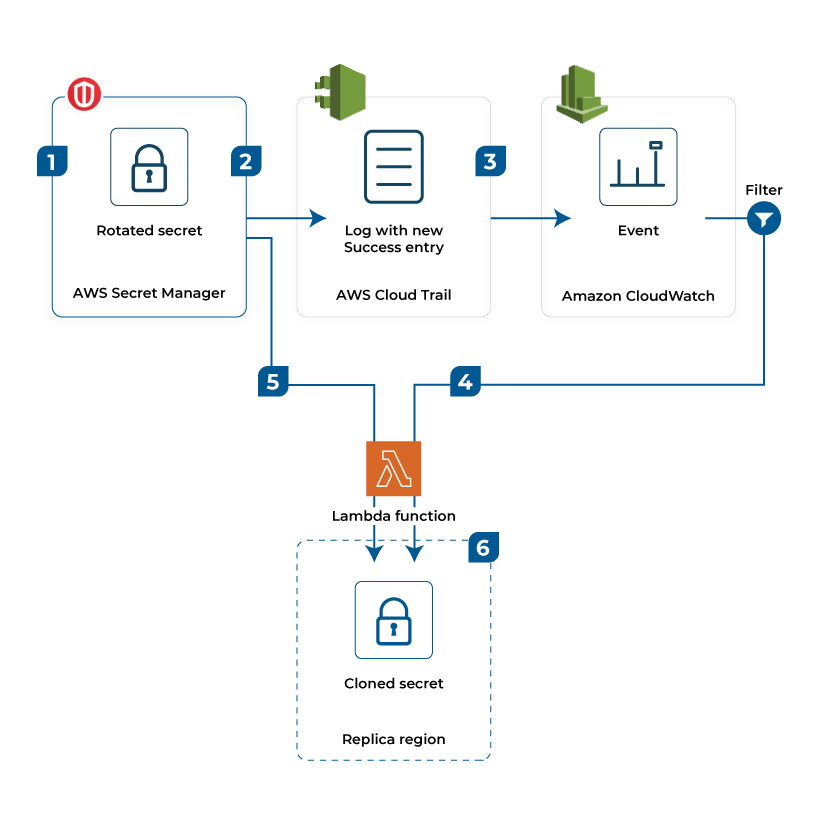
Login credentials play a crucial role in securing all the IT infrastructure, including applications, services, and resources. Accounts with strong passwords are difficult to be compromised. The AWS Secrets Manager helps to store the AWS accounts’ credentials and can retrieve them through a simple API call. The companies can utilize The AWS secrets manager to secure other secrets, such as files and documents protected through the least privilege principle. It enables automatic rotation of the database credentials, protecting the secrets from data breaches.
The above image explains the rotation of the secrets by utilizing the Lambda function. Here, the secrets are stored in duplicate locations, thus protecting them from cyber-attacks. It enables speedy recovery of data in case of data breach or theft.
AWS Certificate Manager
The SSL/TLS certificate establishes a secured connection over the internet. It is used as an identity for the legitimacy of the websites or applications. The AWS Certificate Manager helps to issue, deploy, and maintain the digital certificates of either websites or applications. It also facilitates the automatic renewal of the SSL certificates. These certificates can be used in the private network with the help of AWS CloudFront or AWS Load Balancer. The AWS certificate manager also supports the third-party certificates, but it automatically renews those certificates.
The above image explains the working of the AWS certificate manager in the private cloud environment.
AWS Artifact
The Artifact is an AWS service that provides the AWS security and compliance documents on the demand of the users. It helps the companies to monitor their AWS compliance through regular auditing. These compliance documents include service organization control (SOC) reports, AWS ISO certifications, payment card industry (PCI) reports, and other AWS security documents. But the AWS artifact is only responsible for the compliance of the AWS infrastructure, whereas the company is responsible for its regulatory compliance.
Benefits of AWS Security Services
The AWS security service has various advantages over the traditional security methods. Some of the major benefits of AWS security are mentioned.
Better Monitoring and Control
The AWS security provides better visibility over the data stored in the cloud platform, which helps to identify the vulnerabilities easily. The services like AWS Config and Amazon Cloud Directory enable data categorization based on confidentiality and significance. It facilitates continuous monitoring along with control over the data. The AWS also provides IAM (identity access management), ensuring the right access to the right individual or system. It reduces the burdens of users like physical monitoring of data and control over the data in the on-premises network.
Flexible Services
The major advantage of AWS security is that one can avail of it based on the nature and requirements of the business. Not every business needs high-level security for its cloud infrastructure. For example, the organizations dealing with private information such as personal identification, intellectual property, and financial information should be more secure when compared to other companies that have public information.
Scalability
The customers can scale the AWS security features according to the demand of the business. In the cloud structure, the size of the resources adopted by the companies does not remain constant. The AWS security services can also be increased or downsized depending on the business need. If there is a sudden spike in the business, the cloud resources can be increased along with the security features.
High Efficiency
The cloud services are quite different from on-premises Infrastructure and the security requirements. Thus, the AWS security features provide customized security for the cloud infrastructure, which is highly efficient. It uses the latest technologies to monitor the database activity and detect the cyber threat in the early stage. Due to this, the threats can be identified and mitigated with ease.
Easy to Incorporate
It is difficult to implement security solutions to the present workflow as it requires implementing huge changes in the current Infrastructure. But the AWS security services are easy to adopt and integrate into any cloud server without the need for infrastructural changes.
Supports Third-Party Security Providers
As AWS supports a huge ecosystem of third-party providers, non-AWS users can also integrate the AWS security solutions from their trusted service provider. In this way, the users can utilize the benefits of AWS security without changing their trusted service providers.
Cost-Effective
Pay as you go is the main motto of AWS cloud computing. Thus, the AWS security service is also based on the same model. By using this security, the users can pay only for their services. It saves a huge chunk of money from establishing physical security infrastructure and maintenance.
Security Compliance
The AWS security facilitates compliance management by monitoring the compliance requirement of the resource. As AWS has integrated many regulatory compliances, the companies adhere to the compliance by default. It secures the cloud infrastructure from external threats as well as internal vulnerabilities.
Automation and Machine Learning
With the development of technologies, hackers have also created sophisticated methods to execute cyber-attacks. So, organizations cannot afford to make a human error in cloud security. Thus, the latest technologies such as automation and machine learning (ML) are adopted.
AWS Cloud Security Best Practices
Many organizations are moving towards cloud infrastructure for their business requirements. So, it is essential to understand the cloud services to implement proper security measures to secure the cloud database. Here are a few important best practices that one can use to secure the AWS cloud infrastructure.
- It is essential to have a well-defined security strategy for effective cloud security. Utilizing all the AWS security tools and techniques without a proper plan is time and resource. Thus, the company should have a security scheme before adopting the AWS security services.
- Identify the assets that need to be secured. Proper visibility over the cloud network is essential to secure the infrastructure from threats. Therefore, catalogue the assets base on their purpose and significance.
- One should adopt the security features in all the layers of the cloud infrastructure. A single firewall is insufficient to secure multiple network layers in the AWS cloud. It helps to monitor and control the activities in each layer.
- Limiting access to cloud resources could secure them from cyber threats or data breaches. It is essential to have well-defined Authorization to avoid illegal access to the critical resources.
- Utilizing strong authentication processes like multi-factor authentication will improve the security of the AWS resources.
- Data encryption helps secure sensitive information from getting into the hands of illegal users. So, the customer can use the AWS services like ACM (AWS certificate manager) to encrypt the network connections for AWS websites or applications.
- Take regular backup of the essential data to restore it in case of data breach or theft. The organization can use AWS Backup to manage the backup automatically.
- Make sure to patch the AWS software with regular updates. The operating system or applications without an update is more vulnerable to cyber threats.
- Most security breaches in cloud security occur due to the customer’s mistakes. So, the organization should understand the shared responsibility of AWS and create policies and practices accordingly.
- The companies should understand that security is not one person’s responsibility. So, it is their responsibility to create a security culture that includes all the stakeholders from top to bottom. Train all the employees on AWS security management for better monitoring and control.
Conclusion
Even though AWS provides sophisticated security solutions, it is the responsibility of the user to plan and utilize all those AWS features. By following proper security practices and the AWS security tools, the organizations can secure their resources, which improves the scope of the respective business. It is essential to have a well-established security policy to sustain growth with the cloud infrastructure.