The Cost of a Click: How Phishing Emails Breach Big Brands
Email Phishing has developed into a highly advanced and multi-pronged internet-based threat that affects all major industries. It continues to be the leading cause of data breaches worldwide, from Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report 2024, highlighting an average loss of $1.3 million per Business Email Compromise (BEC) incident.
Phishing involves tricking users into revealing sensitive information or transferring money through deceptive emails, texts or calls. Some popular types of phishing techniques include BEC, voice-based phishing or vishing and stealing login details via fake portals. Threat groups like Scattered Spider and ALPHV/BlackCat are known for combining these tactics with social engineering to bypass even strong security measures.
In this blog, we’ll analyze 10 real-world email phishing cases across finance, healthcare, and public sectors and the lessons they offer for building better defenses.
-
Ireland’s NTMA €5 Million BEC Fraud – July 2025
The National Treasury Management Agency manages Ireland’s national debt. They also oversee state investment vehicles including the Ireland Strategic Investment Fund or ISIF.
Case Summary
Staff received correspondence that appeared tied to an investee company associated with ISIF. The request aligned with the timing that made it seem like a legitimate capital call, leading to funds being released to an attacker‑controlled account before the fraud was detected internally.
What Was Lost
Approximately €5 million was fraudulently wired after staff processed a payment later found to be illegitimate.
Who Did It
Attribution remains unconfirmed, but investigators classify it as a Business Email Compromise or BEC style phishing fraud.
Impact
NTMA launched an urgent review of payment and email security controls. They are working with law enforcement to pursue recovery options.
Key Insight
Enforce strict DMARC to reduce spoofed email risk. Require out‑of‑band callback verification for capital calls or bank detail changes; use dual/segmented approval workflows for high‑value transfers and train finance teams on BEC attacks.
-
Qantas Email Phishing + Vishing by Scattered Spider – July 2025
Qantas Airways is an Australian carrier that serves millions of customers globally. They hold sensitive personal and travel data across its loyalty programs and ticketing systems.
Case Summary
In July 2025, Scattered Spider targeted Qantas with phishing and vishing attacks. Posing as IT support, they tricked employees into sharing MFA codes, then used internal phishing to steal more credentials and gain access to customer data systems.
What Was Targeted or Lost
Attackers compromised internal email systems and approximately 6 million customer records, including contact details and booking information.
Who Did It
A financially motivated cybercrime group is supposedly behind this attack. Multiple speculations suggest Scattered Spider group can be behind this attack who are known for targeting aviation sectors.
Impact
The incident led to significant operational disruption, customer trust erosion, and regulatory investigations into data protection practices.
Key Insight
Multi-factor authentication is not foolproof if employees can be manipulated. Use phishing-resistant MFA like hardware tokens, implement strong user awareness training, and monitor for anomalous login patterns, especially after voice-based social-engineering attempts.
-
The UK’s Co-op Data Theft via Email Phishing – April 2025
The Co‑operative Group is a major UK retailer and consumer services organization with over 6 million members, operating in food retail, insurance, and funeral care services.
Case Summary
In April 2025, Co‑op faced a phishing attack that breached internal email systems. Posing as IT staff, attackers stole employee logins, extracted sensitive member data, and disrupted customer service operations, leading to significant slowdowns.
What Was Targeted
Personal data of approximately 6.5 million members, including names, addresses, and contact details, was compromised.
Who Did It
While it is not yet officially confirmed, threat intelligence suggests Scattered Spider, who is known for targeting high-profile enterprises in the UK and Europe behind this attack.
Impact
No financial data was impacted, but the breach caused reputational damage and compliance investigations, along with high incident response costs. The absence of cyber insurance made the recovery process even more challenging.
Key Insight
Regular phishing simulation training and email gateway filtering with advanced threat detection, along with prompt reporting mechanisms, can reduce risk. Organizations must also segregate sensitive customer data to minimize exposure from compromised accounts.
-
Troy Hunt’s Mailchimp Credentials Stolen via Email Phishing – March 2025
Troy Hunt, one of the most recognized names in cybersecurity, created ‘Have I Been Pwned’ to help people find out if their data was exposed in a breach. His newsletter is widely trusted by professionals who want reliable security insights.
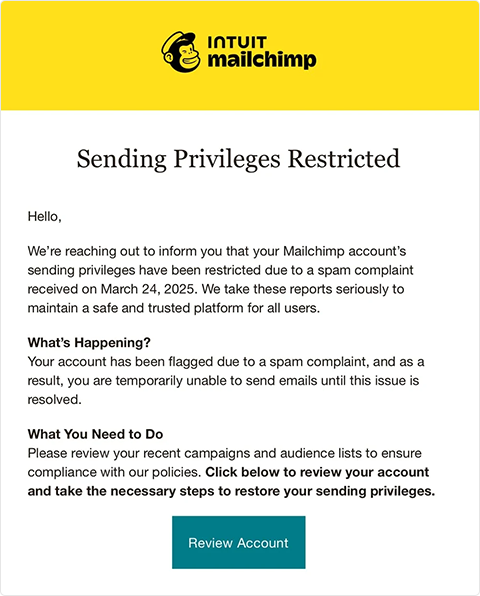
Example of a phishing email impersonating Mailchimp with a fake link to review account access. Case Summary
In March 2025, Hunt fell victim to a phishing email claiming his Mailchimp account was “restricted due to spam.” The fake login page captured his credentials, giving attackers access to subscriber data. HIBP remained secure, protected by separate systems and stronger security layers.
What Was Lost
The compromise exposed credentials for Hunt’s Mailchimp account and approximately 16,000 subscriber email addresses.
Who Did It
Attribution remains unclear, but the attack is believed to have been conducted by professional phishing actors targeting high-profile tech personalities.
Impact
HIBP’s essential services remained unaffected. This hack demonstrated how even seasoned cybersecurity professionals can become targets of deceptively disguised phishing scams.
Key Insight
Phishing can trick even the best security experts. Simple steps like using a password manager with domain checks, enabling hardware-based MFA, and confirming suspicious emails with the service provider can make a big difference.
-
Episource of UnitedHealth subsidiary Healthcare Data Breach – Jan-Feb 2025
Episource, a subsidiary of Optum under UnitedHealth Group, provides risk adjustment, analytics, and data management services for healthcare organizations across the United States.
Case Summary
Between January and February of 2025, attackers most likely utilized phishing to get into Episource’s internal email systems. They acquired patient data in secret for weeks before being caught, proving that healthcare organizations are a prime target for cybercriminals due to the significance of medical data.
What Was Targeted
The breach exposed personal and medical data of approximately 5.4 million individuals, including names, dates of birth, addresses, and Social Security numbers.
Who Did It
Although the threat actors are still unknown, the attack had the characteristics of a financially driven organization with experience in phishing in the healthcare industry.
Impact
Class-action lawsuits, regulatory scrutiny under HIPAA, and the expense of providing affected patients with identity protection services were all consequences of the release of private health and identification data.
Key Insight
Healthcare firms should deploy advanced email security measures, implement zero-trust principles for internal access, and conduct regular phishing awareness training to mitigate credential harvesting attacks.
-
HMRC Tax Account Hijacking and Fraudulent Claims 2024–2025
HM Revenue & Customs or HMRC is the UK’s tax authority, managing income tax, VAT, and various government benefits for millions of taxpayers.
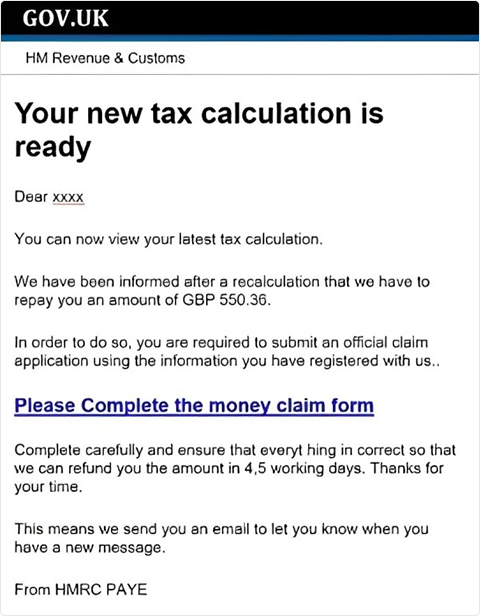
Phishing email example spoofing HMRC, urging users to claim a fake tax refund via link. Case Summary
From 2024 to 2025, a Romanian-led crew blasted out emails and SMS messages that looked like HMRC. Many UK taxpayers clicked and entered their personal information and logins. With that access, the attackers got into tax accounts and filed bogus refund claims. Timing the scam around tax deadlines made it even more convincing.
What Was Targeted or Lost
Around 100,000 taxpayer accounts were compromised, leading to approximately £47 million in fraudulent PAYE, VAT, and child benefit claims.
Who Did It
A Romanian cybercrime syndicate known for orchestrating tax fraud operations across Europe.
Impact
The attack caused substantial financial loss to HMRC and forced the tax authority to invest heavily in fraud detection, account recovery, and public awareness campaigns.
Key Insight
Public sector organizations should enforce strong identity verification, like multi-step authentication, monitor for anomalies in claims submissions, and launch timely awareness campaigns during peak phishing seasons.
-
Change Healthcare’s Credentials & Ransomware – February 2024
Change Healthcare, a key healthcare technology firm and subsidiary of Optum, processes billing, payment, and patient data for healthcare providers across the United States.
Case Summary
The ALPHV/BlackCat group gained access to internal systems in February 2024, ransomware was released, and employee login credentials were stolen via phishing emails. Long delays in payments and patient care resulted from the attack’s closure of hospitals and clinics billing and claims systems.
What Was Targeted or Lost
The attack compromised employee credentials, healthcare data of approximately 100 million users, and disrupted billing operations. A $22 million ransom was reportedly paid to restore services.
Who Did It
ALPHV/BlackCat, a ransomware as a service group known for high-profile attacks in the healthcare and finance sectors.
Impact
Change Healthcare also faced multiple regulatory investigations along with massive operational downtime. This came with long term reputational damage and a ransom payment.
Key Insight
Use phishing resistant MFA as ransomware often starts with simple phishing. Monitor for unusual authentication attempts and enforce least privilege policies to prevent lateral movement inside networks.
-
Orion Chemical’s $60 Million in Email Phishing – August 2024
Orion Chemical is a global manufacturer specializing in industrial chemicals with a large network of suppliers, distributors, and international financial transactions.
Case Summary
In August 2024, attackers tricked a finance employee into authorizing a large wire transfer by using spear phishing emails that imitated a reliable provider.
What Was Targeted or Lost
The company lost $60 million through fraudulent wire transfers following a targeted BEC attack.
Who Did It
A sophisticated financially motivated cybercriminal group likely operating across multiple jurisdictions.
Impact
Orion Chemical’s financial loss was one of the largest recorded BEC scams which forced the company to strengthen treasury controls and seek legal action against banks and intermediaries.
Key Insight
Even experienced finance teams can fall for well-crafted phishing. Multi-person approval for high-value transfers, vendor verification calls, and anomaly detection on payment workflows are critical to mitigating such risks.
-
Snowflake Customers via Scattered Spider 2023–2024
Snowflake is a leading cloud-based data platform serving hundreds of enterprise customers across industries, including finance, retail, and technology. Its platform stores massive volumes of sensitive business data.
Case Summary
Scattered Spider ran credential phishing attacks between 2023 and 2024 against Snowflake customer employees. Stolen login from non MFA accounts gave attackers access to sensitive data which exposed cascading risk of interconnected SaaS providers and their clients.
What Was Targeted
Multiple Snowflake enterprise customer’s cloud data was compromised with threat actors accessing sensitive corporate and customer information.
Who Did It
The attack is likely linked to Scattered Spider, known for multi-vector phishing and exploiting cloud authentication weaknesses.
Impact
Several Snowflake clients reported data theft and regulatory concerns. The incident underscored the need for stronger customer-side security practices in cloud ecosystems.
Key Insight
Phishing resistant MFA for all cloud, monitoring suspicious login across SaaS platforms and auditing access rights should be enforced by organizations.
-
Southern Oregon University $1.9 Million BEC Loss – April 2017
Southern Oregon University is a public liberal arts university in Ashland, Oregon, with thousands of students and a broad network of vendors and contractors.
Case Summary
In April 2017, attackers pretending to be a construction contractor tricked a university’s finance team into sending payments using fake invoices. The scam wasn’t discovered until the money had been moved through multiple accounts, leaving no chance of recovery.
What Was Lost
The university lost $1.9 million after processing fraudulent payments to a scammer’s account.
Who Did It
BEC scammers, likely part of a financially motivated cybercrime group specializing in vendor impersonation schemes.
Impact
The loss strained the university’s budget and led to an extensive review of its vendor payment procedures, as well as tighter coordination with law enforcement.
Key Insight
Always verify changes to vendor banking details through a trusted, separate communication channel. Implement multi-step approvals for high-value payments and employ payment fraud detection systems that can flag anomalies in invoice patterns.
Conclusion
The ten case studies highlight that no organization or individual is immune, regardless of size, sector, or technical maturity, from phishing attacks. From government bodies like HMRC to high-profile companies like Qantas and healthcare giants like Change Healthcare, attackers continue to exploit the weakest link – human trust.
What’s clear is that phishing tactics are evolving beyond generic emails to include multi-channel social engineering such as vishing and smishing, combined with advanced credential harvesting. Cases like Orion Chemical’s $60 million loss and NTMA’s €5 million BEC scam reveal how quickly a single email can escalate into a financial crisis. Beyond monetary losses, breaches often result in regulatory penalties, brand damage, and operational downtime.
Related Articles: