AI tools are now prevalent across industries. People accept their role in transforming business and driving innovation. These tools use advanced algorithms and machine learning. They improve tasks, analyse vast data, and extract rare, valuable intelligence. In 2022, 35% of global companies used AI tools. Sixty-one per cent of employees said AI boosted their productivity.
AI tools are now famous, but there are also growing concerns about the cybersecurity risks associated with AI tools.
AI technologies manage sensitive data, networks, and other AI tools. That’s why, they are prime targets for cybercriminals. However, the tools carry some risk. Therefore, expert advice should be followed to minimize harm.
This blog will address these concerns. It will provide effective cyber security tips for the AI tool and its cyberspace. These guidelines will help users reduce AI tool risks. They will protect their info and systems from intrusion and exposure.
What is an Artificial Intelligence Tool?
An AI tool is a software or a system that uses AI to perform tasks or help with decisions. These tools aim to mimic human intelligence. They should perform tasks that usually require human thought. These tasks include understanding language, recognizing patterns, and making predictions.
AI tools use algorithms and models to analyze and interpret data. They can quickly process data, and find patterns and links related. They generate insights or predictions based on what they learned.
AI tools can enhance efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in various domains. However, we must consider the ethical issues in AI, including data privacy and bias. We must ensure that AI tools are used fairly and responsibly.
How Does an AI Tool Work?
AI tools use techniques and algorithms to analyze data. They find patterns and make predictions or decisions. Let us see a simplified overview of how AI tools typically work.
Data Collection
AI tools need significant data to learn from. They can collect data from databases, sensors, or the Internet, or take time series data in bulk. Data can be structured (having a defined format) or unstructured (text, images, videos).
Data Pre-processing
Before analysis, the collected data is cleaned, transformed, and organized. Data pre-processing includes removing noise, handling missing values, and standardizing the data, it ensures quality and consistency.
Algorithm Selection
AI tool uses particular algorithms to solve tasks or problems. Neural networks, decision trees, and support vector machines are all machine-learning algorithms.
Training and Learning
AI tools use collected and pre-processed data to train their algorithms. They learn from the data by identifying patterns, relationships, and correlations. This process involves adjusting the algorithm’s parameters. The goal is to optimize its performance on the task.
Prediction or Decision-Making
Once trained, AI tools can apply their knowledge to new, unseen data. They use the trained algorithms to analyse the data, generating predictions, classifications, or decisions.
Feedback and Iteration
AI tools often receive feedback on their predictions or decisions. This feedback updates and refines the algorithms, improving their accuracy.
AI tools can work differently based on their design and purpose. Some AI tools may use rule-based systems or expert knowledge, others use deep learning with neural networks.
Applications of AI Tools
Many industries are using AI tools. They are changing how we work, make decisions, and solve problems. Here are the significant areas where tools have helped AI make a significant difference!
Healthcare
AI tools analyse medical images, enabling more accurate results for cancer diagnoses and others. They can predict patient outcomes, aid drug discovery, and suggest treatments. AI chatbots and virtual nurses engage patients. They check and advise on fundamental medical issues.
Finance
AI tools help organizations detect fraud, assess risk, and trade algorithms. They analyze vast financial data for patterns and anomalies, which helps detect fraud early. AI-driven investment assistants use AI, it gives advice based on users’ risk profiles and market analysis.
Retail and E-commerce
AI tools are used for demand forecasting, inventory management, and personalized marketing. Customer product preferences and behaviour are analysed by recommendation systems to recommend specific products. Visual search technology allows users to find products based on images, enhancing the shopping experience.
Manufacturing
AI tools enable predictive maintenance by analysing sensor data to catch equipment failures before they occur. It decreases downtime and optimizes maintenance schedules. Computer vision systems ensure quality control by identifying product defects during production. AI-driven robots automate repetitive and dangerous tasks, improving safe and efficient conditions.
Transportation and Logistics
AI tools optimize route planning, scheduling, and logistics operations. They analyze real-time data, like traffic patterns and weather conditions. It helps them recommend the best routes and reduce delivery times. Autonomous vehicles are used in AI-related algorithms for navigation and ‘object detection.’
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP-based AI tools are used in applications like, Language Translation, Sentiment Analysis, and Chatbots. Now, NLP is being used by Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. They know what to do and understand and how to respond to queries. NLP can summarize text, create content, and extract info from unstructured data.
Education
They use AI for Personalized Learning, Adaptive Assessments, and Intelligent Tutoring Systems. They use student performance data to recommend feedback, which helps them tailor assistance. AI language platforms help learners improve their language skills. They use interactive exercises and personalized instruction, to accomplish their goal.
Agriculture
AI tools help optimize crop management by analyzing data from sensors, drones, and satellites. They provide insights into soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. It helps farmers to make informed irrigation, fertilization, and pest control decisions. AI-powered robotic systems are also used for precision farming tasks like planting and harvesting.
Cybersecurity
Thus, AI tools are potent tools in cyber threat detection and prevention. They look at user behavior, network traffic, and system logs to find anomalies and possible security breaches. AI algorithms can quickly adapt to new attack patterns and detect unknown threats, boosting security.
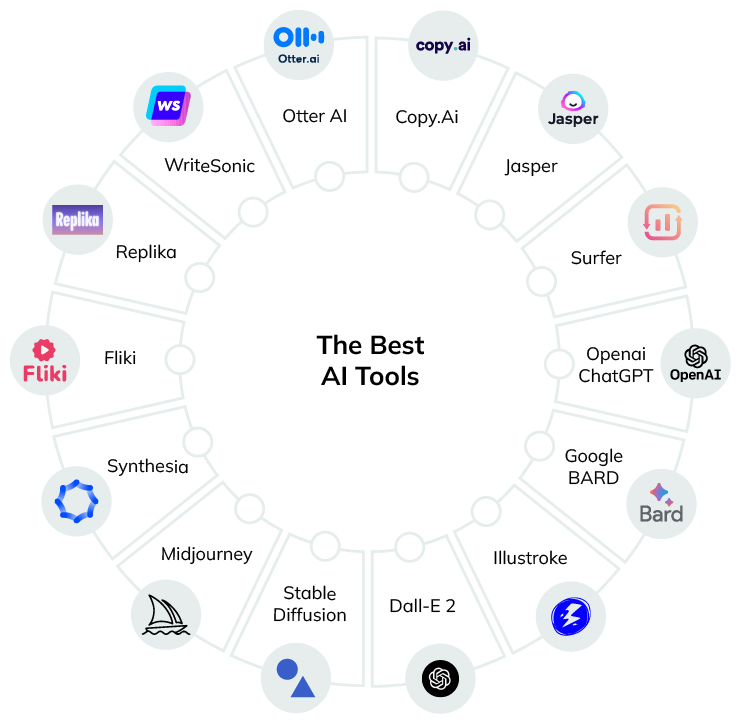
Ordinary people also use the AI tools for various purposes. Some of them are in the image below.
This is how AI tools are changing industries and even people’s everyday lives. As technology and AI progress, many industries will see more AI apps. This will boost automation, efficiency, and innovation.
How is AI Transforming the World?
It is truly going to be an AI revolution. It changes many aspects of man’s life.
One significant impact of AI is automation. AI systems can use machine learning to perform tasks that require humans. This has made industries more efficient and cheaper.
Moreover, AI is enhancing decision-making processes. AI algorithms analyse huge amount of data and expose the patterns, and through that they can come up with important insights and predictions. This empowers businesses and individuals to make informed choices, optimize strategies, and mitigate risks.
It is changing how we interact with technology. NLP lets voice assistants and chatbots understand and respond to human queries, to improve user experience. In these AI based recommendation systems, content or products are given recommendations that can lead to enhance customer engagement and satisfaction. Advancing autonomous vehicles, robotics, and smart home devices is what it’s driving. It’s making our lives easier.
What are the benefits of AI tools?
AI tools use advanced algorithms and machine learning, benefiting many factors. We will explore the benefits of AI tools. The contributions they make go further than simply driving innovation and solving complex problems; they can increase productivity.
-
Automation and Efficiency
AI tools are best for automating repetitive, mundane things. They give humans more free time to work on important, creative work. Automation made through AI makes the process more efficient and productive. How does it? It streamlines workflows and lowers human error. Data entry and support can be automated to save a business time and money.
-
Enhanced Decision-Making
Big data can be quickly analyzed with AI tools. Organizations can then make informed and data-driven decisions with this approach. Machine learning algorithms identify patterns, anomaly spotters, and trend predictors. Businesses have an advantage due to it. There are AI tools that give you real-time information. Its abilities allow decision-makers to respond rapidly and make evidence-based questions.
-
Personalization and Customer Experience
AI tools mostly drive businesses to deliver personalized experiences to customers at scale. AI algorithms look at customer’s behaviour, purchase history, and interests. They then provide tailored recommendations and targeted marketing. Your prospects get instant, personalized support, increasing satisfaction and loyalty from them.
-
Improved Healthcare
AI tools could revolutionize healthcare. They can improve diagnosis, drug discovery, and patient care. Machine learning algorithms analyse medical images thoroughly, assisting in early disease detection. Predictive AI models can predict at-risk patients and engage in proactive interventions. In addition, AI tools can accelerate drug discovery by analysing biomedical data for potential drug candidates.
-
Increased Cybersecurity
AI tools can detect and reduce security breaches, which is vital in an age of rising cyber threats. Network traffic analysis in real time is carried out by machine learning algorithms. They highlight anomalies and detect potential cyber-attacks. Security systems are constantly learning and getting better and are increasingly powered by AI. They give organizations proactive defence and faster responses to cyber incidents.
-
Enhanced Education and Learning
AI tools transform education. They provide personalized learning, competent tutoring, and adaptive tests. AI-powered platforms analyze students’ performance data, identifying strengths and weaknesses for tailored learning content. Intelligent tutoring systems provide personalized help, boosting self-paced learning and improving results.
-
Sustainable Development
AI tools help sustainable development by optimizing resources, energy use, and conservation efforts. AI algorithms analyze data to optimize logistics, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste. AI-powered smart grid systems manage energy distribution, promoting renewables and cutting carbon emissions.
AI tools offer many benefits. They automate tasks, improve decisions, personalize customer experiences, and enhance healthcare. And they are driving innovation by solving complex problems, transforming industries and improving quality of life. It is time we used AI ethically and responsibly. Harnessing its power for society’s benefit is vital.
Top AI Tools to Consider in 2026
Copy.Ai
Copy.ai is an AI-powered writing tool for blogs, review articles, and social media posts. Running on ChatGPT models for NLP, it helps users create top-quality copy for social media, blogs, and ads. Its templates and prompts allow users to beat writer’s block and boost productivity.
Specialized templates are available for specific industries, like e-commerce and real estate. These make it a versatile tool for professionals in various fields. It comes with both free plans and paid versions. While the free version is best for personal use, the paid version is advisable for business operations.
Jasper
Jasper is an AI-driven voice assistant developed by OpenAI. It leverages deep learning techniques to understand and respond to user queries conversationally. Jasper can answer questions, give recommendations, and execute voice commands. It is helpful for hands-free interactions and voice-controlled devices.
It is trained on the LibriSpeech dataset. It has over 1,000 hours of multilingual audiobooks. It can understand different accents and languages, giving users a seamless voice assistant experience across diverse backgrounds. Jasper comes with different paid plans suitable for different purposes.
Surfer
Surfer is a free, AI-powered SEO tool that helps optimize web content for search engines. It reviews top pages and suggests ways to improve on-page SEO, keyword usage, and content. Surfer also helps content creators and SEO pros to improve their websites’ visibility and rankings. It does this with data-driven insights and suggestions.
Surfer’s suggestions come from a data-driven analysis of top-ranking web pages. It gives tips to optimize your title tags, Meta descriptions, and headers. It also covers content length, which helps users align their content.
Openai ChatGPT
The conversational AI tool ChatGPT allows users to interact and talk in a very interactive and dynamic way. It leverages advanced language models to give people human-like responses, enabling natural conversations.
Typical uses include chatbots, virtual assistants, and customer support. It can understand queries and provide relevant answers in conversational interfaces. It can have back-and-forth discussions and handle context switches. It can also show a personality that matches user preferences, creating a more personalized chat experience.
Google Gemini
Google Gemini is an AI tool by Google, that helps people with reading difficulties. It uses machine learning to read web pages aloud for real-time help. Our hope is to enhance the accessibility and inclusivity. We want to help users with reading challenges better understand online content. It uses Google’s text-to-speech technology, which employs WaveNet. An advanced neural network produces natural-sounding speech. Google has made it accessible for users.
Illustroke
Illustroke is a paid AI-powered drawing tool designed to assist artists and creatives. It uses machine learning to analyze sketches and suggest ways to enhance or complete the art.
Illustroke can suggest detailed outlines, shading, and textures. This lets artists explore ideas and improve their digital art. It saves artists time and inspires creativity. It offers new ideas and techniques that artists might not have considered, helping them explore new artistic directions.
Dall-E 2
DALL-E 2 uses the text prompts to produce unique, original, creative images. It uses various concepts and ideas to create visually coherent and extravagant images.
DALL-E 2 is a tool for making art, design ideas, and visual stories. It pushes the limits of AI-generated images, which has a limitation of air art. This produces beautiful, strange pictures from whatever it gleans. It sparks creativity and leads to visual stories. Users are given free credits each month with the tool. If users want bulk images, they should buy extra credits for an unlimited number of creations.
Stable Diffusion
Stable diffusion is an AI technique used for image processing and enhancement. It uses diffusion models to denoise and enhance images. It can remove artifacts, reduce noise, and sharpen images. Therefore, it is a valuable tool for photographers, designers, and image restorers.
Stable diffusion uses models, like the denoising diffusion model, to improve image quality and preserve key details. By iteratively applying diffusion processes, stable diffusion can create great images. It reduces noise and improves clarity, enhancing the visual experience. There is a capacity of both free and paid versions.
Midjourney
Midjourney is an AI analytics platform. It provides insights into user behavior and customer journeys. It then utilizes machine learning to analyse the interactions of users. It finds patterns and optimizes customer experiences.
Midjourney offers insights into the customer journey. It also allows businesses to know what is working well and how they can improve engagement, conversion rates, and customer preferences. Moreover, they can then make data-driven decisions to improve their products or services.
Synthesia
Synthesia is a paid AI tool that creates realistic videos with virtual presenters. It uses deep learning to map human actors’ movements and expressions onto avatars, creating engaging, personalized videos.
Synthesia is used in video production, personalized marketing, and virtual presenters. It creates custom videos for various other services. It helps businesses and creators captivate audiences with unique, custom videos. Their videos do stand out in many online platforms.
Fliki
Fliki is an AI tool for text-to-speech and text-to-video. It helps users create audio and video content easily. The tool’s vision and mission are to create audio and video content in minutes with the power of AI.
Users can use tools to generate quality, engaging, and valuable content at scale. Whether you are a business owner or a content creator, this tool has everything you need. It helps you create engaging social media content and generate videos quickly.
Replika
Replika is an AI-powered Chatbot designed to provide personalized conversations and emotional support. It is an NLP and machine learning based tool to understand the users and have empathetic chats. In addition, it is a free tool. The idea is to provide an environment that is free of prejudice. Users can express themselves and get virtual companionship or therapy.
It aims to provide emotional support and engage in deep talks. It also offers guided self-reflection exercises. It is an excellent tool for those seeking companionship or a place to think. However, due to AI abuse, Replika AI has been restricted. There are paid and free versions.
WriteSonic
WriteSonic is a paid AI tool. It helps write high-quality content, like blog posts and ads.
It leverages language models and data-driven techniques to generate engaging and persuasive text. WriteSonic uses language models and algorithms. It gives users prompts, outlines, and variations to inspire and speed up their writing. It saves time and boosts productivity by automating repetitive writing tasks. This is perfect for content creators, marketers and for anyone who needs a hand with writing and wants to create persuasive, engaging text.
Otter AI
Otter AI is a popular transcription tool offering free and paid plans. It transcribes audio and video recordings into accurate text.
It uses advanced speech recognition and machine learning to transcribe speech. This makes it easier to search, edit, and analyze recorded conversations or meetings. Otter AI is great for notetaking, transcribing interviews, and accessibility. It creates searchable archives of audio content.
What are the potential cybersecurity risks associated with AI tools?
AI brings several cybersecurity threats that anybody working in an organization or an individual facing a computer must be aware of.
Here are some of the risks linked to AI tools.
Adversarial Attacks
Adversarial attacks exploit AI systems by manipulating inputs to deceive the algorithms. These attacks can cause AI models to make wrong decisions. This may lead to security breaches. For example, an autonomous vehicle’s object recognition system could be fooled. It might misidentify road signs or pedestrians.
Data Poisoning
AI models rely on large datasets for training. An attacker can harm a model by manipulating its training data or trick an AI system by injecting malicious data into its training set. This can cause the system to make wrong decisions or take harmful actions.
Model Theft
AI models often represent valuable intellectual property. Unauthorized access lets attackers reverse-engineer and copy AI systems, harming intellectual property and security. It could also be used for some malicious reasons. Model theft can cause financial losses and a loss of edge. It can also create counterfeit AI systems.
Privacy Breaches
AI systems often need access to large amounts of personal or sensitive data. Weak safeguards for data handling expose sensitive information to breaches, jeopardizing privacy. Robust security protocols are vital. They protect data from unauthorized access. It’s then stored, processed, and transmitted.
A common vulnerability in AI systems can enable attackers to access personal data or conduct surveillance.
Unintended Consequences
AI systems, like chatbots and autonomous devices, may behave unpredictably and have biases that pose security risks. These accidental significances can arise from flawed algorithms, biased data, or poor testing. For instance, a Chatbot may unintentionally disclose sensitive information, and an autonomous system may make harmful, incorrect decisions.
Lack Of Explainability
For example, some AI models such as deep neural networks are black boxes, making it hard to understand how they make decisions. This lack of interpretability can hinder detecting and mitigating security vulnerabilities. Attackers can exploit this opacity to bypass security measures or launch stealthy attacks.
Scalability of Attacks
AI tech enables automation and scale. It lets attackers launch large, efficient attacks. For instance, AI bots can perform other attacks, such as credential stuffing, DDoS, and phishing attacks. Failure to understand the potential of the AI concept can lead to an exponentiation of cyber-attacks and the rate at which they are executed.
How to Use AI Tools Safely? A Complete Guide
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) tools grows more widely, we must prioritize security measures. It can protect sensitive data and AI systems.
Some of the best security practices are mentioned below.
Choose popular AI tools
When choosing AI tools, pick well-known, reputed providers. With a proven record of accomplishment for security and reliability. Popular tools have many users; therefore, vulnerabilities are more likely to be found and fixed. In addition, trusted tools often undergo rigorous security tests, which reduces the risk of exploits.
Update and patch AI tools regularly
Regular updates and patches are crucial for maintaining the security of AI tools. Providers often release updates to fix security flaws and bugs, which hackers could exploit. In some cases, enable automatic updates whenever possible so that you don’t need to go hunting for the latest security patch every time. Keep updating regularly and check for updates and apply it to lower an attack risk.
Implement Strong Passwords
Strong, unique passwords are vital. They protect your AI tools and accounts. Here everything is explained about password security.
- Passwords to be used should be at least eight characters long. They must combine both the case letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Do not use simple passwords that anyone could guess, such as “1234” or “password.” Use a password manager that will automatically produce and keep strong passwords for you.
- Always enable multi-factor authentication where available it adds extra security. What it needs is a second step, such as a code sent to your mobile device, in addition to your password.
Restrict Unauthorized Access
It is important to enable strict access control to prevent unauthorized access. Another is to grant users access based on the least privileged access approach. Users should only have the permissions required to do their tasks. Regularly review and update user access rights to match their job roles.
Segment AI tool networks to limit access to authorized individuals or systems. This helps contain potential breaches and prevent lateral movement within the network. Implement the RBAC policies to allow these activities to occur. Restrict RBAC by allowing these activities to occur. User roles and permissions should be assigned to their tasks. This ensures that users have appropriate access privileges aligned with their job functions. Check user activity, access logs, and system logs. This helps detect and investigate unauthorized access attempts.
Regularly watch and audit AI tool usage.
Check and audit your AI tools to ensure security. This includes reviewing access logs, activity logs, and user permissions regularly. By quickly spotting any suspicious activity, you can act to reduce security threats.
Secure Data Storage and Transmission
When working with artificial intelligence tools, always be careful where your data is stored and how it is transferred. Make sure that certain information is protected with an algorithm when stored and while being transmitted. Encrypt information at a high level, accepted in the sphere, to prevent unauthorized access.
Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Perform periodic security assessments of your AI tools to identify and address vulnerabilities. It can involve penetration testing, code review, and vulnerability scanning. Engage with experienced security pros or external auditors. They can assess the security of your AI tools.
Stay Informed About Emerging Threats
Implement continuous threat intelligence monitoring to stay updated with the latest security threats. Rapid risk response hinges on vigilant tracking of trustworthy Intel. Security bulletins and threat feeds offer vital, timely insights for organizations to act swiftly against emerging dangers.
In addition, info-sharing networks and threat Intel communities can provide valuable insights. Proactive security measures protect AI tools from evolving threats. Therefore, we must regularly analyze and act on the gathered threat intelligence.
These practices can greatly lower the risk of your users getting unauthorized access. They will protect sensitive AI data and maintain the integrity of AI tools.
The Need for Cybersecurity Awareness and Training among AI Tool Users
As AI tools become more common in industries, users should be aware of cybersecurity. Training is now critical, as cyber threats become more sophisticated, we must educate users. Users need to understand and reduce potential risks.
Human Element
The biggest vulnerability in any network is usually the users. Terrorists exploit or take advantage of human vulnerabilities. They use phishing, social engineering, and unauthorized access attempts. Cybersecurity training enables users to understand and handle emergent threats.
Protecting Sensitive Data
AI systems process enormous volumes of confidential information daily. This spans individuals’ private details, corporate proprietary knowledge, and intellectual property. As AI tech advances, it will integrate more into businesses and personal lives. For this reason, this data must be protected. These powerful tools must force the evolution of security measures. They must protect sensitive information from breaches or misuse. Users’ lack of cybersecurity awareness can lead to data breaches. This can expose confidential information. Training users on data protection best practices helps protect sensitive data from leaks and hacks.
Identifying and Preventing Cyber Attacks
The reason is that there are more and more attackers and attackers have adopted multiple approaches to an organization’s compromise. Cyber security familiarizes the targets with such attacks and combats them with attacks such as malware, ransomware, and phishing. It also covered training to help the targets. They also identify the signals that attackers possess for users.
Ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements
Strict data privacy rules exist in many industries, including GDPR and HIPAA. Training in cybersecurity teaches users what they need to do and how to follow regulations. It also avoids possible penalties that can prove costly and damage their reputation.
Mitigating Insider Threats
Insider threats are a huge security risk to the security of AI tools, whether intentional or not. Employees with the right can quickly disclose non-public information because they have the right to access AI. This is because they can be tricked with social engineering attacks. Educating users can decrease the occurrence of insider threats. Knowing the importance of their data privacy and the risks of their actions, they should know what they are doing.
Promoting a Culture of Security
Training and awareness of cybersecurity help develop a culture of security in the organization. By knowing the risks and best practices, users help guard against AI Tool Security. This security culture fosters a shared responsibility among users. They become vigilant and proactive in spotting and reporting potential security incidents.
Enhancing Incident Response
Although implemented with solid security, incidents can still take place. Security training increases the response to security incidents. It minimizes the impact and ensures a quick, coordinated response. A breach can still be contained with trained users. They cut downtime and costs.
Adapting to Evolving Threats
Attackers frequently develop new ways to attack. Cybersecurity awareness and training programs update users, on security best practices, help users adapt to new threats, and boost their ability to spot and respond to new attack methods.
In the age of AI tools, cybersecurity training is vital. It protects data, reduces cyber threats, and ensures security. Organizations can educate users on risks and best practices and foster a security culture, making users the first line of defence against cyber threats.
Future Directions and Recommendations For AI Tools
As the use of AI tools continues to grow, ensuring their secure usage becomes paramount. Organizations must act to avoid cyber threats and protect sensitive data. This section explores future directions and recommends ways to use AI tools securely.
Enhanced Security Testing and Assurance
It is crucial to test and ensure the security of AI tools. It includes penetration testing, vulnerability assessments, and code reviews for AI systems. Complex AI systems demand comprehensive security. Every component, from algorithms to interfaces, requires rigorous testing. Interconnected parts create new vulnerabilities. Thorough analysis protects against evolving threats. Robust safeguards are essential for trustworthy AI. They include algorithms, data inputs, models, and the underlying infrastructure.
Privacy-Preserving AI Techniques
Privacy concerns are a growing issue in the AI landscape. Organizations should invest in privacy-preserving AI. It protects sensitive data while enabling AI. Federated learning, differential privacy, secure multi-party computation, and others. They preserve privacy during data training, model sharing, and inference.
Secure Data Governance and Management
AI systems depend wholly on data. To protect AI tools, you must set up robust data governance and management practices. These include data classification, encryption, and data lifecycle management, but they also include strong access controls. It is necessary to protect personal data according to data privacy laws.
Explainable AI and Transparency
The problem with AI algorithms is that they are not transparent and interpretable. We need to develop and adopt explainable AI techniques. These techniques show how AI models make decisions. They help users verify the outputs. Explainable AI builds trust. It aids error analysis and finds biases in AI.
AI-Specific Threat Intelligence and Defense
As AI tools face more cyber threats, we need AI-specific defense. This includes using AI for threat and anomaly detection and monitoring in real-time. Organizations should invest in AI security tools. They can find and respond to attacks that exploit AI flaws.
Collaboration and Information Sharing
The cybersecurity landscape is a collective effort. To avoid new threats, organizations and experts must share information. Organizations should join industry forums and share threat Intelligence and best practices. This will improve the security of AI tools.
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Continuous monitoring and incident response are vital. Which enables quick detection & response of security incidents. AI tools must have strong monitoring. This should include real-time log analysis, anomaly detection, and behaviour-based alerts. Organizations should have clear incident response plans and drill regularly. This will ensure effective responses to security breaches.
Security-Aware Workforce
Human factors remain critical in ensuring the secure use of AI tools. Organizations should prioritize cybersecurity training to educate employees. Employees must learn the risks, best practices, and their security roles. This can reduce the risk of human-caused breaches. It will also foster a security-minded culture.
Conclusion
These days, AI tools are potent allies in the fast-changing tech world, revolutionizing industries and our interactions with the digital world. As we hope for the promise of these new tools, we must also face their security threats. AI is like a double-edged sword. It teaches us how to empower, and it can teach us how to enable evildoers as well. The future is being built with AI tools, and they must be used wisely and cautiously. The responsibility is ours by using strong security, we can unlock AI’s great potential while safeguarding against its risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are AI Tools a Security Risk?
AI tools themselves are not inherently a security risk. However, like any technology, their usage and implementation can introduce security vulnerabilities if not properly managed. Issues such as insecure data storage, inadequate access controls, and vulnerabilities in AI algorithms or models can pose security risks. Organizations must prioritize secure development practices, regular updates and patching, robust access controls, and ongoing monitoring and testing to mitigate these risks.
What are the Common Risks Involved in AI?
- Data Security and Privacy – Unauthorized access, data breaches, and data leakage are significant risks associated with AI systems, particularly when handling sensitive or personal information.
- Adversarial Attacks – Adversarial attacks involve manipulating or tricking AI systems by introducing specially crafted inputs or malicious actions. It can lead to AI systems making incorrect or unsafe decisions, impacting the integrity and reliability of the system.
- Model Vulnerabilities – AI models can have vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Model inversion attacks, poisoning attacks, or evasion attacks are examples of threats that can undermine the performance and reliability of AI systems.
- Regulatory and Legal Compliance – AI systems may need to comply with various regulations and legal frameworks, such as data protection laws, intellectual property rights, and fairness and transparency requirements.
How Does AI Pose Privacy Risks?
AI poses privacy risks due to its reliance on vast amounts of data. AI systems often require access to personal or sensitive information to train models or make accurate predictions. This data can include personally identifiable information, medical records, financial data, and more. This data can be subject to unauthorized access, breaches, or misuse if not properly protected.
How to Overcome AI Risks?
Organizations can implement strong data governance practices to overcome AI risks to ensure data privacy and security. Regular audits should be conducted to address biases in AI models, while diverse and representative training data can be used to mitigate bias. Robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and vulnerability assessments, should be employed to protect AI systems and data from breaches. Transparency and explainability should be prioritized, explaining AI outcomes and fostering accountability.
What are the Ethical Risks of AI?
Ethical risks in AI arise from the potential for AI systems to have unintended or harmful consequences on individuals and society. These risks include biases in AI algorithms, which can result in discriminatory outcomes, privacy concerns due to the collection and use of personal data, the potential for job displacement and economic inequality, and the erosion of human autonomy and decision-making. Ethical risks also include AI-enabled surveillance, manipulation of public opinion, and the lack of transparency and accountability in AI systems.