The Ultimate Guide on Information Management – Benefits, Best Practices, & Data Security
An old saying “Information is Wealth” is more pressing than ever in the current business trend. The companies which make use of such valuable data are becoming successful among their competitors. This marks the importance of information management which forms a system to handle the data from creation to destruction. This document covers the topics of information management, data management, information lifecycle, benefits, best practices in information management, etc.
What is Information Management
For every organization, information is a more asset that includes both physical and digital forms. In order to utilize the information, it is indispensable to create a process to collect, protect, store and distribute the information within the organization. This process is known as information management. It facilitates the availability of the right information to the right person at the right time which is important for a successful business. Information management involves managing all types of information such as data, paper, files, e-documents, audio, video, etc. In simple terms, information management is an accumulation of information from multiple sources and the transfer of information to multiple users. It is also called information lifecycle management as it helps the organization to manage the information throughout the information cycle.
The Information management has four major components.
-
People
The people who are involved in the Information management including the designer of IM and the users.
-
Policies and Processes
It includes the rules and procedures laid for entire information cycle. This makes sure that right information is available to the right persons.
-
Technology
It includes both physical as well as virtual aspects that support the latest technologies. Examples, computers, other electronic devices, software used, etc. Usage of the latest technology facilitates the process of information.
-
Data and Information
It is the primary input for the Information Management without which the entire process is useless.
What is Information Management System?
The information management system (IMS)refers to the software that is designed to store, organize, retrieve, and share information. It is a digital method to facilitate the management of information. The types of information that can be processed include text, numbers, audio files, images, video, etc.
The information management system database is incorporated with segment or block which forms the base of the hierarchical model. The segment is comprised of many fragments of data called fields. At the higher level, the segment is called as root segment. The segment of a particular segment is known as the child segment which determines the order in the database.
Data vs Information
Under the common pretext, both data and information look like synonyms, but they are not. Data only refers to the digital format of the formation that can be easily used in a computing network. Whereas, information incorporates all the other forms including the data. In other words, information involves the process of understand the data to create valuable information for the organization. Data is useless unless it is turned into useful information.
Difference Between Information Management and Data Management
| Information Management | Data Management |
|---|---|
| The information management includes the process of collecting, handling, storing and using the information in all possible formats. | Data management is a subset of information management which makes a specific data of the company to be precise, absolute, safe and available. |
| All information is not data. It includes both physical and digital form of information. | All data is an information. It is a form of information in binary digits which is only understandable through computing. |
| Information is derived from various forms of data collected from different sources which can be utilised for the well-being of the organisation. | Data is a single attribute that proves to be useful only when transformed into information. |
| The information management framework of an organisation makes it capable of managing the information along its entire life cycle. | The data management framework involves procedure, policies and practices to manage the data life cycle. From file-naming to documentation of metadata. |
| Examples, document management, digital asset management, web content management, etc. | Example, database management system, data security, data source identification, etc. |
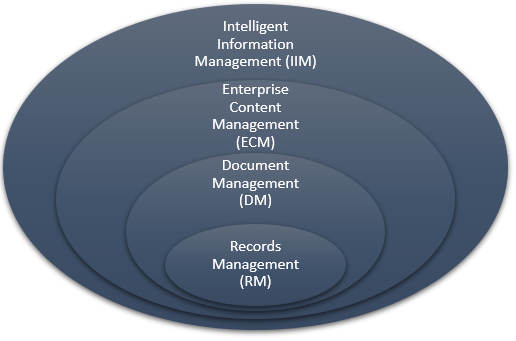
Intelligent Information Management
It is known that the information involves both structured and unstructured formats. The unstructured includes documents, paper works, written contents, etc, while the structured includes databases, spreadsheets, e-files, etc. Until recent years, unstructured information formed the major part of the organization which was managed using Enterprise Content Management (ECM). The ECM only manages content ignoring the relative data.
The digital revolution has changed the process of information management in organizations. The data is completely digitized with the use of cloud-based services which increase the amount of data to be handled by the organizations. The Intelligent Information Management (IIM) is a successor of Enterprise Content Management (ECM) which deals with the management of structured as well as unstructured information. Information management is not a single process but an incorporation of several process management within the organization. For example, Document Management (DM), Records Management (RM), Web content management, digital asset management, Learning management systems, intranet platform, etc, all come under Information management.
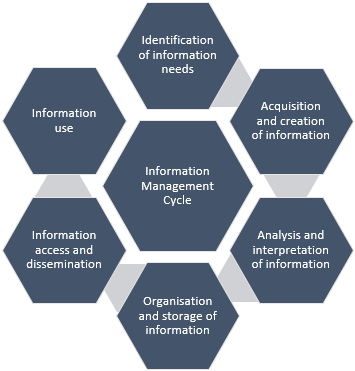
Key Areas of Information Management
Information management includes several key areas which define the way of information processing within the organization. It is a step-by-step exercise where one concept facilities the working of the other. They are explained below.
-
Need for Information
The initial step is to find the need for the information. The company should be aware of the information required for the smooth operation of the business. It gives a basic idea upon which the information management can be planned.
-
Deriving the Intent
To implement the management framework effectively, it is essential to have a clear goal that drives the data utilization. Absence of any clear vision will make the information management pointless.
-
Budget Analysis
Any business project starts with the budget setting. It is the amount of money the company is willing to spend on the system implementation. The information management method will be designed based on the available budget. It includes setting up costs, operational and maintenance costs.
-
Choice of Technology
The choice of technology is purely based on the budget limit. The latest technologies such as artificial intelligence, automation, etc, are capital intensive which can be adopted based on the company’s investment capacity.
-
Source of Information
After finishing the preliminary task, the actual information management starts with determining the source of information. The source of information depends on the need for the data. It could be from various sources such as internal source, staffs, competitor analysis, market research, etc.
-
Categorizing the Data
The next step is to define a method to collect and categorize the data. It also includes other aspects such as the quantity of information, frequency, time, etc. The collected information can be classified based on the classifications such as demographic, technical, financial, etc.
-
Data Sharing
The main intent of information management is to retrieve and share information effectively. The method of sharing will be clearly defined in the system. Creating two or more channels will facilitate easy sharing of information which improves the working efficiency.
-
Implementation
The implementation of the information management is not a one-time process. The system should be evaluated regularly to find out any loopholes.
-
Maintenance
It helps to keep the data management updated with new methods and technologies. Regular maintenance of the information management framework improves productivity and efficiency which gives a sustainable triumph in business.
The Need for Information Management
The information forms the backbone of the organization which plays a significant role in its success. Proper management of the information is essential to make the business more profitable. There are various factors that contribute to the need for a reliable information management system.
- The need for such data management starts with the digitization of the world. Any business that does not adapt to the latest technology will be pushed by the competitors. Digitization of data is essential for a successful business.
- Nowadays, companies are handling a large amount of data that can’t be stored in the physical which makes it difficult to be accessed. So, other alternatives such as cloud storage are required to store such a huge amount of data.
- The productivity of any business is increased only when the data can be accessed easily. If the required data is not available when needed, it affects the efficiency of the employees.
- The data analysis is essential to form the business strategies and make important decisions. It gives a clear idea about the issues and solutions for the business.
- To reduce the risk by utilizing the available data. This can be achieved by proper information management.
- To secure important information such as financial, legal, intellectual property, etc, from any data breach.
- The basic idea under the adoption of the information management system is to get more profit with less investment.
Benefits of Information Management
-
Shrink in Operational Cost
The moto of any business is to get more returns on less investment. Information management is one of the best ways to reduce operational costs. The data is an asset irrespective of the type of business and the data management cycle requires huge capital which can be reduced by implementing an appropriate information management system. This makes the process of storing, retrieving, and sharing data uncomplicated which saves more time and money.
-
Raised Returns
More returns can be obtained by utilizing the resources more effectively. The data should be stored in such a manner that the employees should not waste time in searching for the information. In a business, every minute is money, more time spent on searching for the required data reduces the overall productivity. Information management reduces the searching time by making data available to the right person at right time. This in turn improves the quality of work that results in high returns.
-
Risk Mitigation
Unexpected risks have the capacity to paralyze business activity. The proper management of information can reduce the fear of risks by conducting a proper analysis. Well-executed information management will provide a timely update of possible risk factors that could affect the business. By just managing the available data, billions of dollars can be saved by mitigating the risks that are backed by better decisions. This improves the recovery time when affected by unavoidable risks.
-
Verified Regulatory Procedures
A business that works with clearly defined rules and procedures will be highly productive when compared with a business without any standard framework. Information management is one such system that incorporates certain regulatory compliance to improve efficiency. It saves the employees from confusion regarding the management of data that ultimately prevent data breach.
-
Use of Latest Technologies
To put up with competitors in the business world, it is vital to make use of technologies in the working process. Utilizing the latest technologies such as automation, machine learning, artificial intelligence, etc could pave way for better usage of information to make a fortune in the business. Information management is a whole package of regulatory procedures backed by the latest technologies that will help to stay ahead of the competitors.
-
Enhanced Productivity
The lesser the time taken to retrieve and share the required data, the higher will be the productivity. It is made possible by using a better information management system. It allows the sharing of information through various channels that increase the coordination among the teams. Data utilization plays an important role in the performance of the business.
-
Protection to Sensitive Information
Careless handling of crucial information may result in a data breach that leads to financial loss and reputation loss. Confidential data such as proprietary information, intellectual property, etc, should be protected from third-party access. This can be fulfilled using information management where the important information is protected by limiting the access and establishing a procedure to gain the access to such information.
-
Sustained Growth
The management data is rewarded by sustained growth in the business. Following a defined regulatory procedure aided by the latest technology will help the organization to maintain sustainable growth.
-
Innovation in Business
By getting access to vital information, it is easy to understand the market needs and plan accordingly. This helps to influence innovations in the products and services. Better utilization of data gives a big picture of future trends in the business. A business that fails to adopt the changes will be out of the race. Innovative methods in data management will also help to get more returns.
Best Practice of Information Management
It is important to have a sound Information management practice for success in business. As information forms the basis for all business irrespective of the products (physical or virtual). Information management does not mean a single solution but a cluster of various systems to fulfill the business needs and address the issues in the organization. Here, are a few information management best practices.
-
Customized Approach
There is no single solution for all information management problems in an organization. The organizational structure is too complex to implement a one-stop solution. It is a challenging task to design and implement the information management project in such a complex environment. But many companies adopt simple solutions such as
- Using a ‘one size fits all approach where a single software or technology is adopted, to solve all the information management problems.
- Following a strict and inflexible solution, not because the information management problems are dynamic across various departments within the organization.
These defects can be overcome by using a customized approach for every problem in information management. The solution should be derived based on the needs and issues where the risk can be mitigated in the project. The implementation should be bottom-up, in which several minor solutions are applied to solve a major problem.
-
Appropriate Implementation
A well-planned information management system is pointless without proper adoption. Installing the latest software all over the computers in the organization doesn’t make any change if it is not used by the employees. To make a fortune from the data, it is essential to educate the employees about the concept of Information management and encourage them to use the related software to process the data. Lack of implementation results in loss of useful information which could be turned into a profit.
For a business, each data is a money making only when converted into useful information. This is possible by adopting an information management system. For example, for an e-commerce company, data regarding customer search is a profit-making strategy. Such data can be made useful only when the data is processed using information management. The adoption of better information management is crucial not only on the financial front but also in the work culture and cyber security front.
-
Prioritised Solution
In an organization, it is not possible to solve all the problems in one shot. Therefore, it is a smart move to prioritize the issues based on the potential to address the business needs. This priority list can be created by conducting research within the company to find out the current issues upon which immediate actions are required. It can also include employees’ point of view to make improvements in information management. Making a priority list helps in concentration on bigger issues first and dealing with less important issues later. For example, the error in managing the customer data should be dealt with prime importance as it could lead to a data breach.
-
One Step at a Time
Many companies seek a single solution such as large software applications or exclusive procedures to solve the entire information management issues. Even though such approaches seem to be efficient to achieve a long-term goal, it fails to give clear guidance to achieve immediate goals. As we discussed earlier, the companies are too complex to design a sole information management solution. The companies trying this approach will get caught in the designing process, so they can’t move any further with implementation.
Instead of trying to design an ideal IM model, the solutions can be applied on the trial-and-error method where different solutions can be adopted to get the best out of it. Addressing smaller problems in a long run could reflect in solving the major problems easily.
-
Clear Vision
Action without a goal is futile. A set a clear vision is the first step to making a business successful. The goal-oriented organization runs more effectively when compared to the aimless business strategies. The full potential of the information management system can be experienced only when it is in alignment with a clear vision. A well-planned information management framework with a clear output will give a big picture of the company’s profit to the employees that could encourage them to implement information management more confidently.
-
Authorised Access
One of the best practices for effective information management is to have authorized access to the data in an organization. It is not necessary for all employees to have access to all kinds of data which leads to misuse of the granted access and at times will result in a data breach or data theft. So, it is essential to categorize the data based on their importance. Confidential information should be accessed only by higher officials. This will prevent the information from getting into the wrong hands. Access to the information should be granted based on the requirements of the employee. Lesser access to sensitive data higher the safety of the information. This can be achieved by creating an implicit user access management system so that the flow of the data can be monitored.
-
Risk Management
There is no business without risk. Forecasting the risks will help the organization to tackle the situation and prevents adverse effects of unexpected issues. Information is no exception for such a scenario. The risks involved in information management are adopting ill-suited technology, high budget, technical difficulty, improper implementation, etc. Before planning desirable information management, the risk factors should be taken into account which is beneficial in risk mitigation. A general method to reduce the risk is to implement a trial-based solution that saves a huge amount in the project budget.
-
Co-ordination
For information management to give a visible result, integration among the different stakeholders is essential. Many department departments are involved to run a business. It is essential to establish coordination between the departments to achieve the adoption of structured information management. The organization system is a composite structure where single control is impossible. A clearly defined objective is adequate to form coordination among the teams. In this way, each team can have its own approach to attain the ultimate goal.
-
Simplifying the Technology
It is easy to adopt complex high-end software for information management purposes. But the positive result is attained only with the use of technology by the staff. The companies should take responsibility to educate the staff to use the installed software. On the other hand, the software should not be too complex which includes difficult rules and procures to use them. The user interface can be simplified so that all the employees could use them easily. Simplifying the technology gains more involvement from the staff.
-
Data Management
The data forms the basic unit of information management. Without data, there is no information to manage. Date management is essential to adopt information management. Various methods can be practiced to manage the data.
-
Metadata
It facilitates the categorization of data which enables quick access. It includes various fields such as creation date, type of data, language, etc. Updated information is much easier to handle which also ensures usability and security.
-
Data Quality
The quality of the data should be checked before using it in information process.
-
Data Sharing
The information management works on data sharing. A seamless data sharing is necessary for a success in business. This can be done by proper data management.
-
Conclusion
Planning and implementation of a better information management system ensure the success of the business. The organization with well-executed data management need not be worried about the utilization of information which helps to a great extent for a business to run. Greater the management of the information, the higher the profit for the company.