SSL certificate or Secure Socket Layer refers to a digital certificate that validates the website’s identity and allows encrypted connection over the website.
Organizations install SSL certificates to secure the data passing between the user and the server. SSL certificate enables padlock on the website to ensure end users that their data is safe over the website. At present, the padlock symbol looks like a settings symbol.
In this article, we will discuss SSL, SSL functionality, importance, and types of SSL in detail.
What is SSL?
SSL is a security protocol. In early times, the data was travelled through insecure HTTP protocol and was at risk of being eavesdropped by any unknown person. After the introduction of SSL (Secure Socket Layer), a cryptographic protocol, the data remains encrypted and enables HTTPS before the domain name. An extra “S” is a symbol of SSL security.
In this way, SSL or Secure Socket Layer creates an encrypted channel in which the data from a client to the server and vice versa travels in an encoded format to avoid eavesdropping.
SSL works on encryption and decryption techniques that encode and decode the data with a private and public key, which we will cover later in this article.
SSL/TLS Protocols
However, SSL works on cryptographic protocols named SSL and TLS protocol. SSL, in the early times, worked on SSL 3.0 protocol. This protocol was deprecated, and a new TLS protocol was introduced by this time.
Essentially, TLS 1.0 was published by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in 1999. The latest TLS 1.3 version was published in 2018. TLS is implemented to encrypt data over application protocols like HTTP, FTP, SMTP, IMAP, UDP, DCCP, and SCTP.
| Protocol | Published Year | Status |
|---|---|---|
| SSL 1.0 | Unpublished | Unpublished |
| SSL 2.0 | 1995 | Deprecated in 2011 |
| SSL 3.0 | 1996 | Deprecated in 2015 |
| TLS 1.0 | 1999 | Deprecated in 2021 |
| TLS 1.1 | 2006 | Deprecated in 2021 |
| TLS 1.2 | 2008 | In use since 2008 |
| TLS 1.3 | 2018 | In use since 2018 |
What is an SSL certificate?
SSL certificate is also named as digital certificate that validates organization’s identity and allows encrypted connection. Organization should buy and install SSL certificate to secure the data flowing between the server and the browser.
Many certificate authorities (CA) offer SSL certificate at different prices. DigiCert, GlobalSign, Comodo, Sectigo, RapidSSL are few famous CA that has been serving to their clients since many years. As per MWR report, DigiCert, GlobalSign, and Comodo are key players in SSL certificate providers.
How do SSL certificates work?
An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that validates an organization’s identity and allows encrypted connection. Organizations should add an SSL certificate to secure the server and browser data.
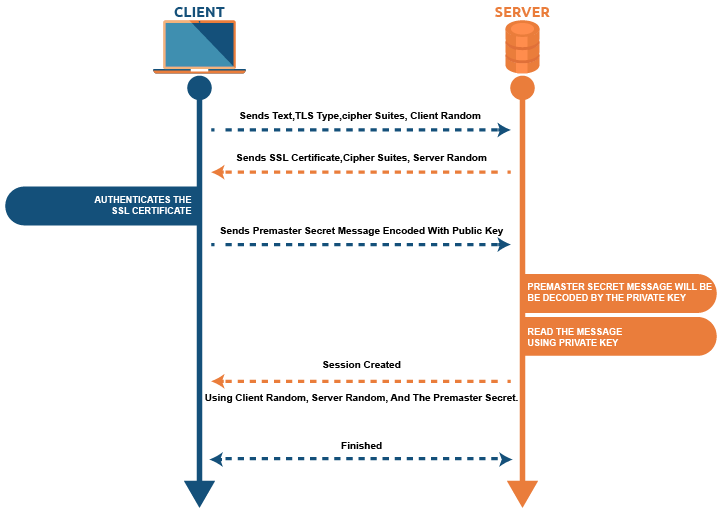
When a browser tries to connect to the website, the browser and the server create an encrypted connection enabled with an SSL certificate. The whole encryption process is called an SSL handshake. However, the process works in the background and is invisible to anyone.
There are three keys: public, private and session keys. The encryption and decryption process works on public and private keys. A public key encrypts the data, which only a private key can decrypt. During SSL handshake process, a session key is created to encode data transition. Here, we have given the SSL handshake process a brief description.
Phase-1: The browser sends a ‘ClientHello’ message to the server, containing information like SSL/TLS supported versions and cypher suites they can use.
Phase-2: The Server sends back a ‘ServerHello’ message to the browser confirming the highest TLS/SSL version and cipher suite that both can support.
Phase 3: The server sends its digital certificate backed and verified by the certificate authority.
Phase-4: Now, the browser verifies the presented SSL certificate. Afterwards, a browser uses the server’s public key to encrypt a session key premaster secret and sends it to the server.
Phase-5: The server then decrypts the premaster secret with the private key. The server and the client use the session key for symmetric encryption for all transactions.
Why do websites need an SSL certificate?
SSL certificate creates a secure connection to ensure end users that the data remains safe during the transition.
If the data remains in plain text, a third party can eavesdrop and modify it. It is hazardous to users’ privacy. HTTP is a protocol that needs security to create a secure environment for the website. To do so, a website holder needs an SSL certificate that protects sensitive information like login credentials and credit or debit cards.
Benefits of SSL Certificate
Encryption
SSL certificates encrypt sensitive data and make it unreadable to third parties. Secure data in transit ensures end users that their data is safe so they can easily positively interact with the website.
Secure Icon
SSL enables a secure icon in the address bar to assure visitors that they are on the secure site and their credentials will remain safe. As a result, the ROI of a business grows over time as more customers join the site.
PCI DSS Standards
SSL certificates are bound by specific rules and regulations called PCI DSS standards. PCI DSS rules by the government state the usage of the latest encryption standard and a secure connection on the website for the interest of visitors and customers.
Business Validation
SSL certificate authority validates business credentials by checking its related documents. It shows end users that they are dealing with the right and verified organization. Their data is safe with the website and protected by strong encryption.
Types and Validation Level of SSL Certificate
SSL certificates fall into three validation categories: Domain validation, organization validation, and extended validation. All SSL certificate types are single-domain, wildcard SSL, and multi-domain SSL certificates. Let us get on their details:
Validation Levels
Domain Validation
Domain Validation is a primary validation type in which the domain ownership is verified by email, CNAME or HTTP verification. The site owner only needs to verify the domain name, and the certificate authority issues an SSL certificate. However, there is a lack of in-depth validation in domain validation. So, if you are keen on higher validation, you should read the validation types.
Organization Validation
Organization Validation is one step ahead of the domain validation type. The certificate authority (CA) requires business and legal documents to verify business identity. Therefore, the certificate owner must validate the domain name and submit documents to the CA. After verification, the certificate authority issues an SSL certificate that should be installed on the server.
Extended Validation
Extended Validation or EV SSL is the highest validation type in which domain and organisation validation processes are included. The extended Validation process offers a site owner a verified legal business identity to ensure end users. A site visitor can check in the browser about a verified business name. The CA can call the registered number for further verification during this process.
SSL Certificate Types
Single Domain SSL Certificate
Single domain SSL certificate secures a single domain only. It can be either domain validation, organization validation or EV SSL certificate. Single-domain SSL is ideal for small or medium businesses.
Multi Domain SSL Certificate
Multi-domain SSL protects different domains and subdomains in a single certificate. It is a cost-effective certificate that saves the expense. For example, domain.com and example.com can be secured with multi-domain SSL. You can include different levels of subdomains in this certificate.
UCC Certificate
UCC or Unified Communication Certificate works like a multi-domain SSL certificate. However, it is best used for Microsoft exchange servers or services. A site holder can secure multiple domains and subdomains with this certificate. It can protect many domains and subdomains with a single certificate.
Wildcard SSL Certificate
Wildcard SSL Certificate is designed to secure the main domain with an asterisk (*) and its first level of subdomains. For example, *.domain.com can secure mail.domain.com, payment.domain.com, and example.domain.com. Wildcard cannot be issued under EV validation, as each subdomain needs to be verified, while in wildcard, only the main domain is verified. However, different levels of subdomains can be covered under multi-domain wildcard SSL.
How does a website obtain an SSL certificate?
- It is easy to get an SSL certificate nowadays. Here, we would like to simplify your purchase process by offering one of the most reliable and cost-efficient SSL providers called SSL2BUY.
- The provider carries customer centric approach and takes care of customers in each SSL purchase stage. For that, a website owner should have a few essential things to obtain an SSL certificate
- An IP address, updated WHOIS record, government registration documents of business, type of validation, type of SSL certificate, and all these things should be ready when a site owner wishes to obtain an SSL certificate.
- Once you select and purchase an SSL, you will have My Account with SSL2BUY, where you can do purchase, renew, reissue and other SSL tasks.
- During configuration process, a site owner first needs to create a Certificate Signing request.
- During the configuration process, you need to submit it to the SSL2BUY.
- Then, complete the configuration process with a domain validation process via email, CNAME or HTTP file verification.
- A site owner should submit required business-related documents in case of Organization or EV validation.
- Once the validation process is completed, the certificate authority issues an SSL certificate that should be installed on the server. The installation process may vary depending on the server type.
- In case, if you find any difficulty during SSL purchase, configuration or installation, SSL2BUY takes care of it by providing 24/7 technical customer support.
Conclusion
SSL certificate uses TLS protocol; your server should have the latest TLS version settings. SSL certificates are essential for security as the cyber world faces daily threats. To continue your business in a secure environment, an SSL certificate is necessary. To win customers’ confidence, SSL acts like a saviour.
FAQs
What is the full form of SSL?
SSL is also called a Secure Socket Layer. It helps to secure the data travels between the server and the browser.
What happens when your SSL certificate expires?
When you use expired SSL certificate, the browser starts showing warning. Users afraid of sharing details on the website as third party can eavesdrop the information. Eavesdropper can spy on the details and misuse against users. Expired SSL certificate should be renewed quickly to retain users’ trust. Else, it will create a false impression of a company and overall ROI gets affected.
Difference between self-signed and CA signed certificates.
Self-signed certificates are created and signed by organizations or individuals themselves. These SSL certs are signed by their private keys. These certificates are not publicly trusted certificates. Websites or browsers do not consider such certificates trustworthy. Self-signed certificates do not have trust indicators as they are signed by individuals/organizations.
On the other hand, CA-signed certificates are the symbol of trust as third-party CA signs and create them. Such SSL certificates carry trust indicators for better security assurance. Mostly browsers, OS trust CA signed certificates. A site owner must pay a fixed amount to purchase a CA-signed certificate. However, CA-signed certificates are available at low cost nowadays.
What is the difference between SSL and TLS certificates?
SSL and TLS certificates are the same as they can be installed on the server to secure the website. However, TLS protocol and SSL protocol are two different things. All modern websites work with TLS protocol as the latest SSL protocol 3.0 was deprecated in early times. You should check TLS version settings to ensure the website uses the TLS version.
Related Articles